Administration
This chapter includes details on how to administrate components of grommunio with the available toolset.
grommunio admin UI (AUI)
After successfully installing the grommunio Appliance, you can access the UI through your browser on port 8080 (8443 with https soon).
Since you most likely set a password for admin UI while installing the Appliance, you can immediately use these credentials to login.

To navigate through the UI, simply use the drawer on the left side of the page.
Dashboard
After a successful login, you can see the dashboard with live data of the machine grommunio runs on.
Antispam
Since grommunio has its own antispam service, according data can be displayed in the Dashboard.

Services
Antispam isn't the only grommunio service, in fact there are lots more. The current state of these services can be seen on the left side of the dashboard.
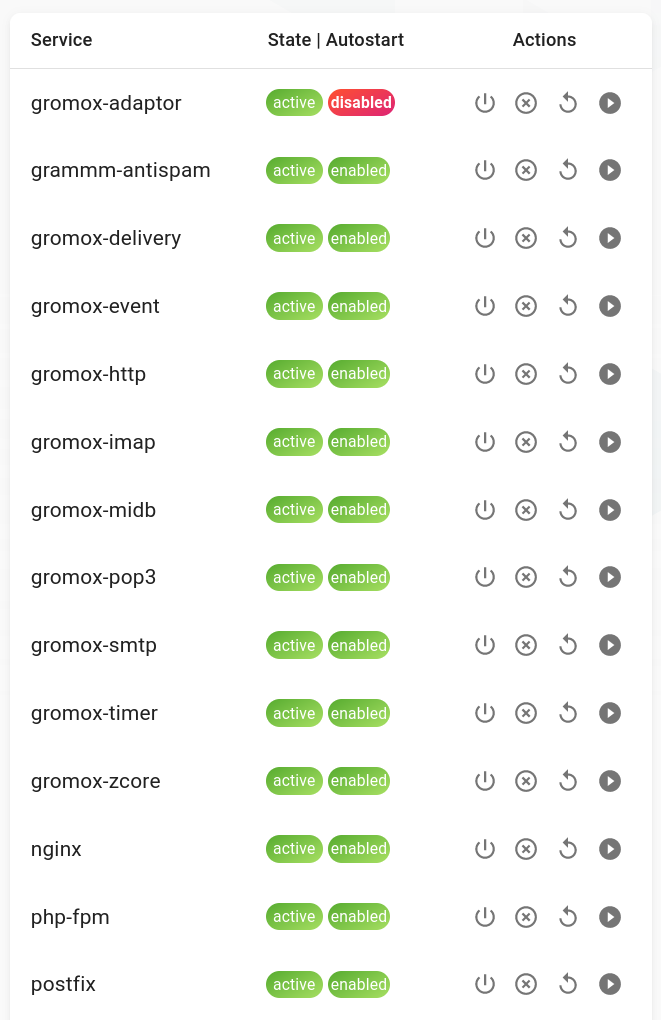
You can stop, restart or start these services from here by clicking the action buttons of a service in the list.
CPU
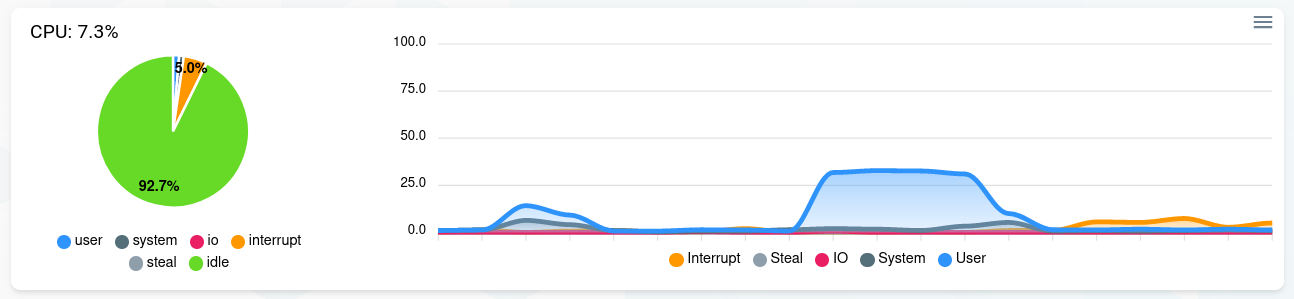
A live and history display of the CPU usage.
Memory
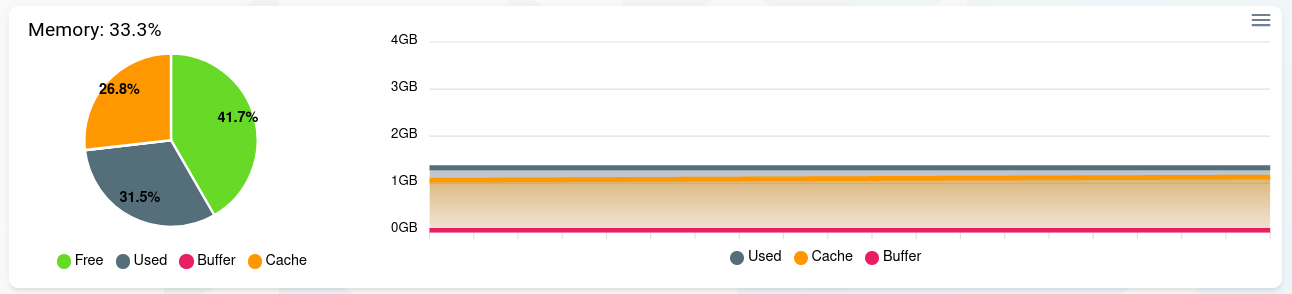
A live and history display of the memory usage.
Disks and swap
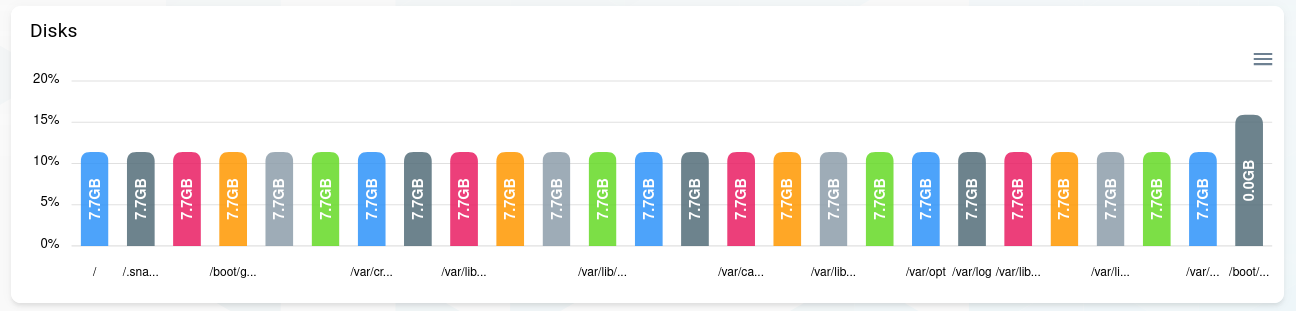
A live display of the disks and swap.
Load
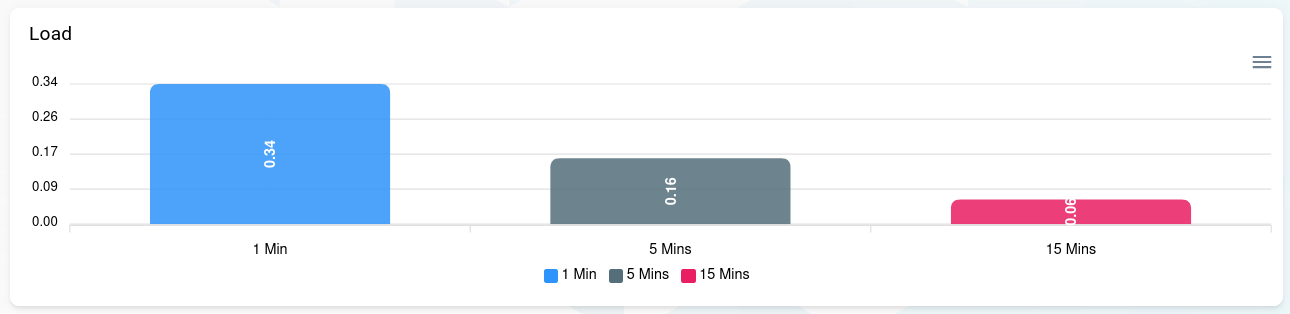
A display of the system load over the last 1, 5 and 15 minutes.
Versions

A display of installed component versions.
Domains
Click on Domains in the drawer, which will redirect you to the list view of existing domains. If you just set up grommunio, the table will be empty. If you want to show currently deactivated domains check the checkbox show deactivated.
Adding a domain
To add a new domain, click the blue NEW DOMAIN button to open the form dialog:
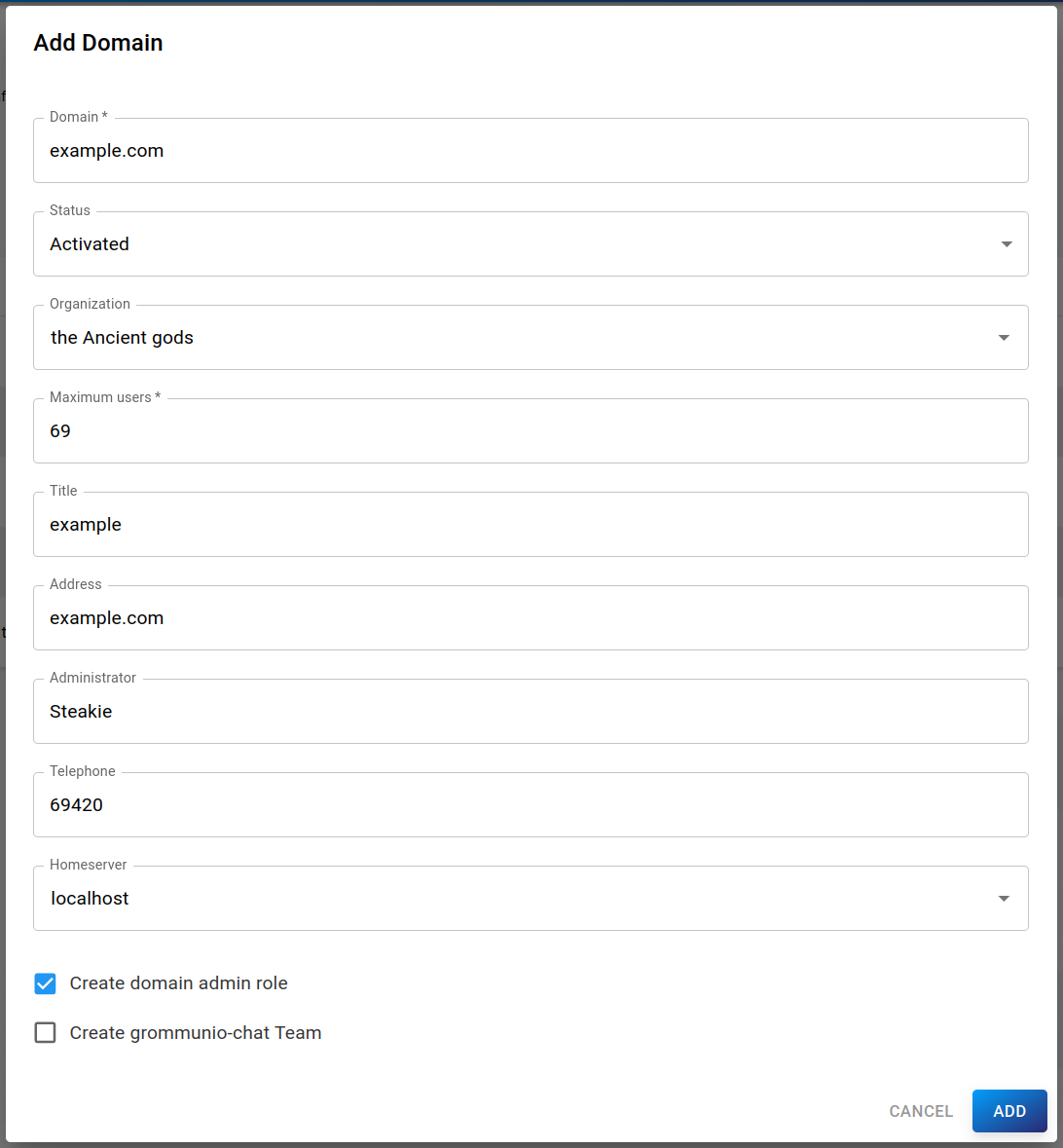
The following properties can be set:
Domain (required): The name of the domain (cannot be changed afterwards)
Status: Whether the domain should be currently activated or deactivated
Organization: Organization of the domain
Maximum users (required): The maximum amount of users (e-mails) of this domain
Title: Title of the domain
Address: Address of the domain
Administrator: Administrator of the domain
Telephone: Hotline for problems
Homeserver: The server on which the domain's data is stored
Create domain admin role: Creates a role for users, who will be admins for this domain
Create grommunio-chat team: Creates a new grommunio-chat team for this domain. If you want users of this domain to be able to log into grommunio-chat, this has to be checked.
Click Add to confirm or Cancel to cancel.
Editing a domain
To edit an existing domain, click on a domain in the list to open the detailed view of a domain.
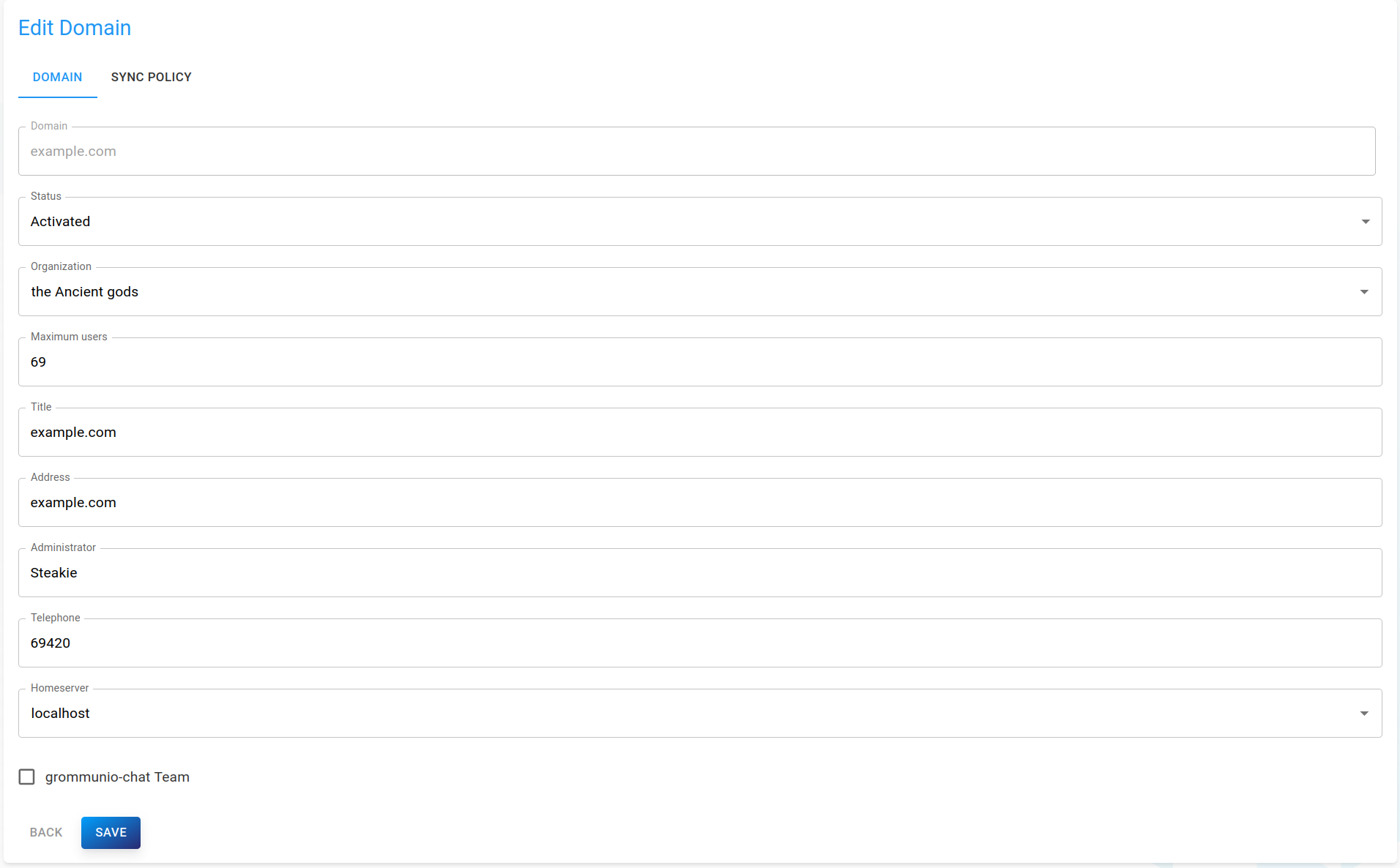
Simply change attributes to your needs, then click Save on the bottom to save your changes.
To change the current password of the domain, click Change password next to the domain name. You will be prompted to set and repeat your new password.
Deleting a domain
To delete a domain, click on the trash icon of a domain in the domain list view.
The following flags can be set:
Delete permanently: Checking this, will completely remove the domain out of the database, not just deactivate it
Delete files: Only available if permanently deleting, will delete all files of this domain
Click Confirm to confirm or Cancel to cancel
Reactivating domains
If you didn't delete a domain permanently, it will automatically be set to deactivated. To reactivate a domain, click on a domain in the list to get to the detailed view. Now change the status from deactivated to activated.
Users
If at least one domain exists in the database, users can be added to a domain. To show existing users of a domain, navigate to the domain view in the drawer (Domains tab).
Click on a domain to expand available sub-pages and click on Users, which will redirect you to the list of users of this domain. If you just installed grommunio or added the domain, the list will be empty.
Alternatively, to see all users across all domains, click on Global users in the drawer.
Adding a user
To add a new user, click the blue NEW USER button to open the form dialog:
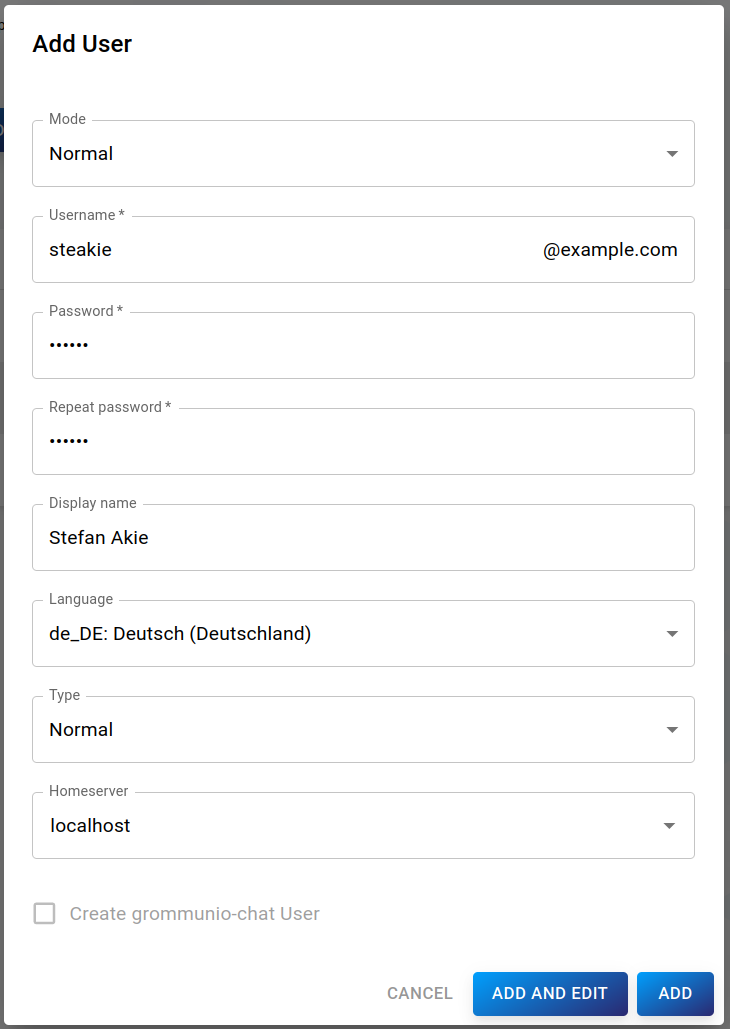
The following properties can be set:
Mode: Normal or shared user
Username (required): Username of the user
Password (required): Password of the user
Display name: Name to be displayed for this user
Storage quota limit: Storage limit of the user
Type: Type of user
Homeserver: The server on which the user's data is stored
Click Add to confirm or Cancel to cancel. If you need to further specify user properties, click Add and Edit to open the detailed view of this user.
Editing a user
To edit an existing user, click on a user in the list to open the detailed view of a user.
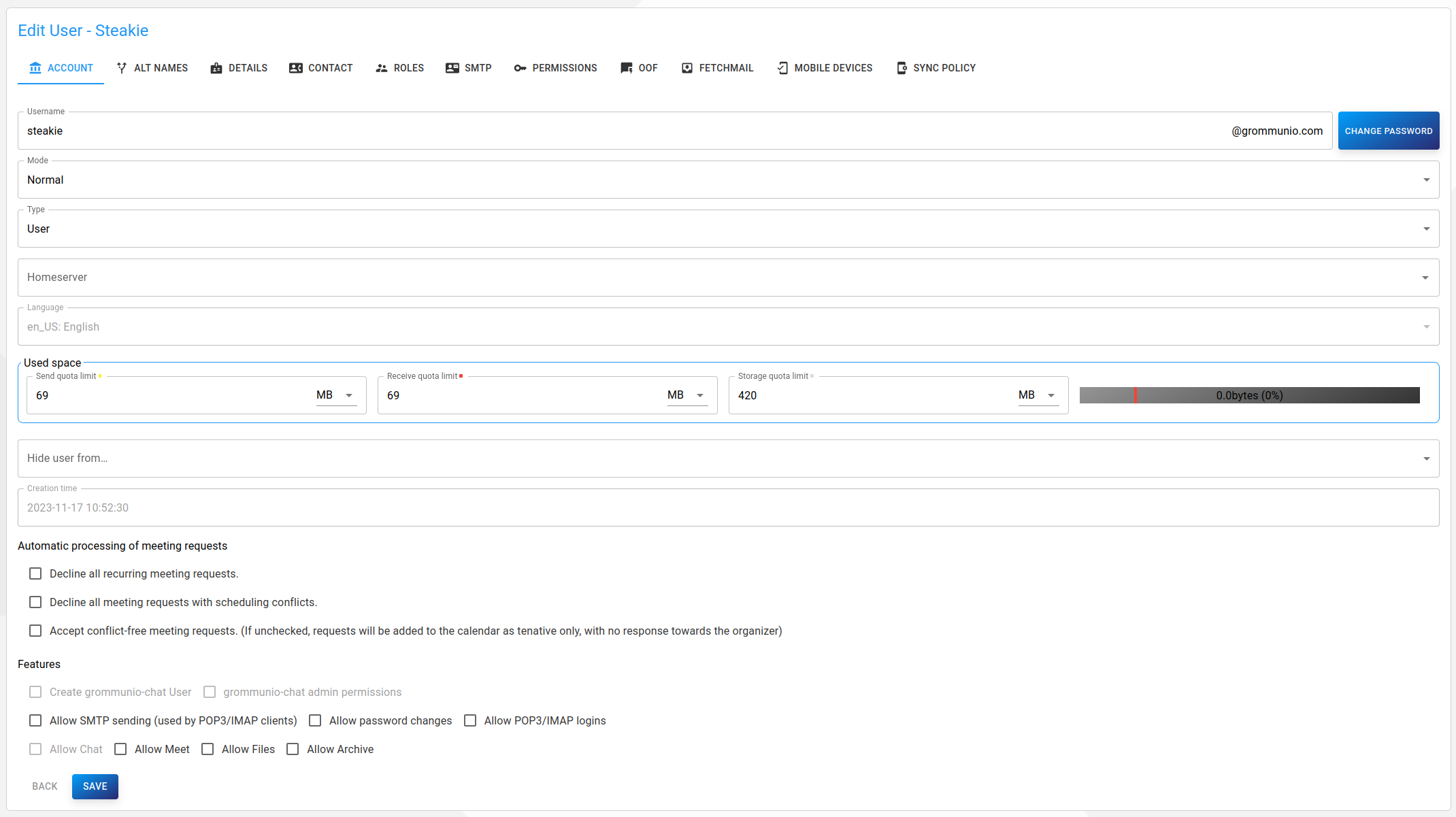
There are 10 main categories of user properties:
Account: RPC/HTTP (Outlook Anywhere), MAPI/HTTP, IMAP, POP3 etc. configuration
Alt names: Alternative usernames to log into mail-clients with (does not have to be an e-mail address)
Details: MAPI props
Contact: Additional MAPI props
Roles: Roles of the user
SMTP: Additional e-mails for this user (aliases) and forwarding rules
Permission: Select users which have special permissions for this user's mailbox
OOF: Out of office settings
Fetchmail: Configuration to fetch mails from other servers via fetchmail
Mobile devices: List of user's mobile devices (via MDM)
Sync policy: MDM sync policy (specifically for this user)
Account
The following properties can be edited:
Username
Mode: Mailbox mode, select between a normal user, a suspended user and a shared mailbox
Type: Type of user
Homeserver: Server on which the user's data is stored
Language: Store language of the user (does not effect the language of the UI)
- Used space
Send quota limit: Maximum size of the mailbox before sending messages is blocked
Receive quota limit: Maximum size of the mailbox before message reception is blocked
Storage quota limit: Maximum size of the mailbox before storing (any kind of) objects is blocked
Hide user from: Hide user from specific user lists (e.g. the global address list)
Automatic processing of meeting requests: Trivial
Create grommunio-chat user: Creates a grommunio-chat account for this user. If this checkbox is disabled, there is no grommunio-chat team for this domain.
grommunio-chat admin permission: Gives administrative permissions for grommunio-chat to this user's grommunio-chat account.
grommunio-chat permissions: Grants grommunio-chat admin permissions
Allow SMTP sending: Allows the user to send e-mails via SMTP
Allow password changes: Allows the user to change his/her password
Allow POP3/IMAP logins: Allows logins via POP3 or IMAP
Hide from GAL: Hides the user from the Global Address List
Allow Chat/Meet/Files/Archive: Allows access to respective feature
Note that, because a message needs to exist internally before it can be sent, the storage quota limit is also relevant for sending. Conversely, for reception, the storage quota limit must allow storing messages. (Thus, the storage quota should always be more than receive quota, and more than send quota.)
To change the current password of the user, click Change password next to the username. You will be prompted to set and repeat the new password.
User & Contact
Common MAPI props. These are self-explanatory.
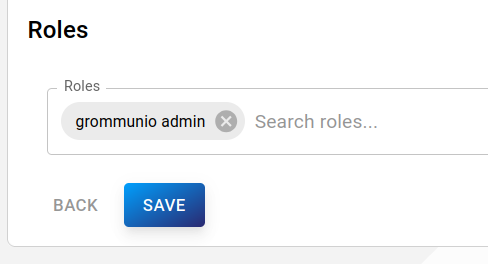
Roles
Roles of the user, which can be edited with the autocompleting textfield
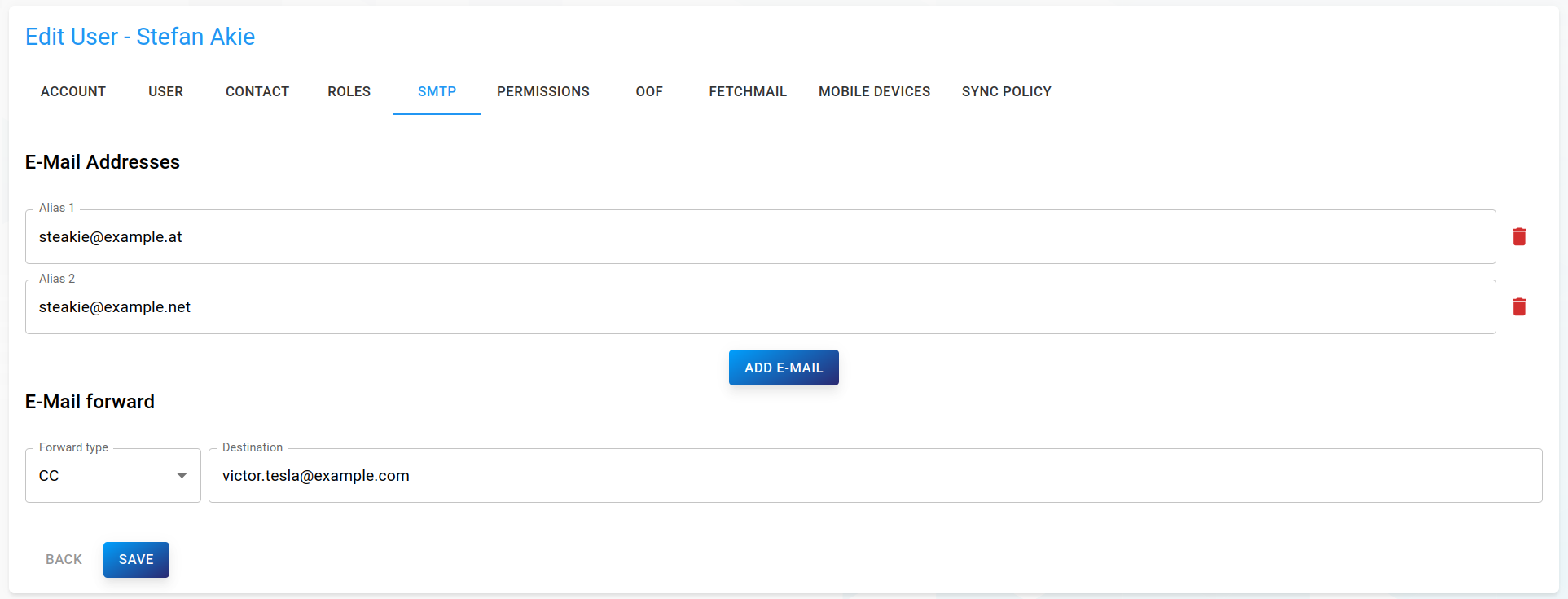
SMTP
User aliases: The textfield(s) can be used to set aliases for the current user. Use the "Add E-Mail" button to add, or the trashcan icon to delete an alias.
E-Mail forward: This can be used to enforce a redirect or message cloning action irrespective of the Inbox Rules configured by a mailbox owner. The mail transfer agent used in your mail system must support this and must be configured accordingly to evaluate the SQL table where the forward info has been stored (see below).
Configuration fragments to implement CC mode (forward_type 0) for e.g. Postfix:
File
/etc/postfix/main.cf: settingrecipient_bcc_maps = mysql:/etc/postfix/grommunio-bcc-forwards.cfFile
grommunio-bcc-forwards.cf: settinguser = ...,password = ...,hosts = localhost,dbname = grommunio,query = SELECT destination FROM forwards WHERE username='%s' AND forward_type = 0
Redirect mode (forward_type 1) is left as an exercise to the administrator.
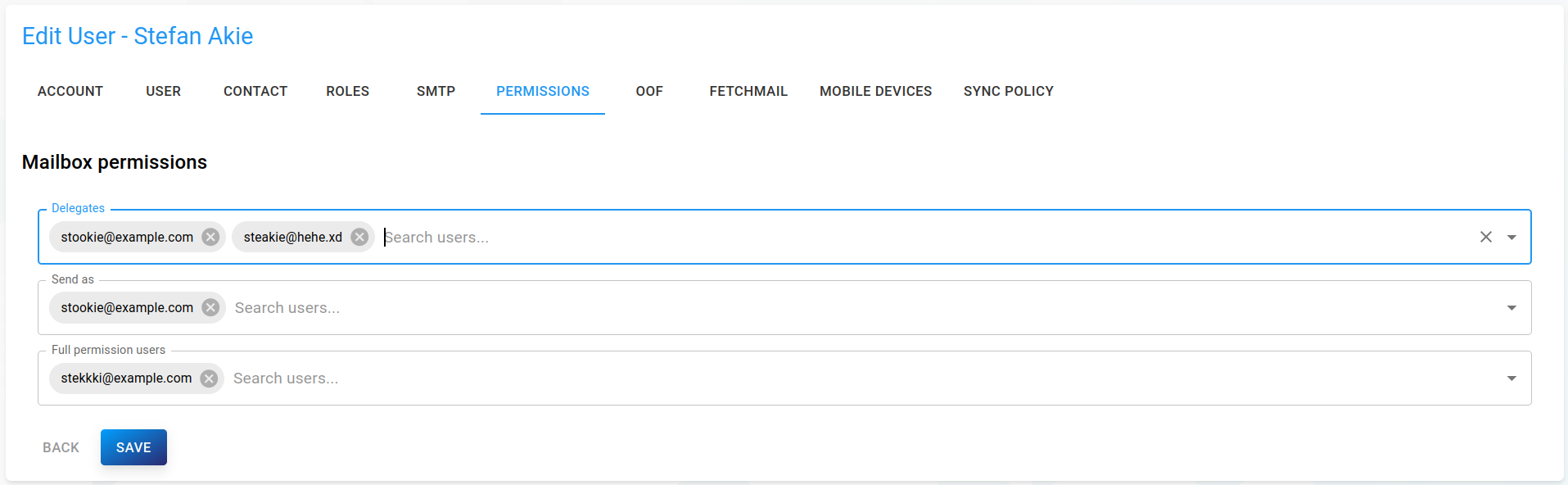
Permissions
This dialog allows giving other user identities certain permissions at the mailbox level.
Delegates: Users in the delegate list may exercise the "send on behalf" feature, i.e. send messages with a
From:line containing the delegator's identity. The use of delegation is recorded in messages.Send As (also known as Impersonation): Users in the send-as list may send messages with a
From:line containing the delegator's identity. It is similar to delegation, but the use of delegation is not recorded in messages. Send-As overrides and masks Send-On-Behalf, because SA/SOB permission is only known server-side and MAPI clients have no way to choose between the two.“Full permissions”: Users in this list will be treated like the mailbox owner and not be subject to permission checks when reading or writing folder or message objects.
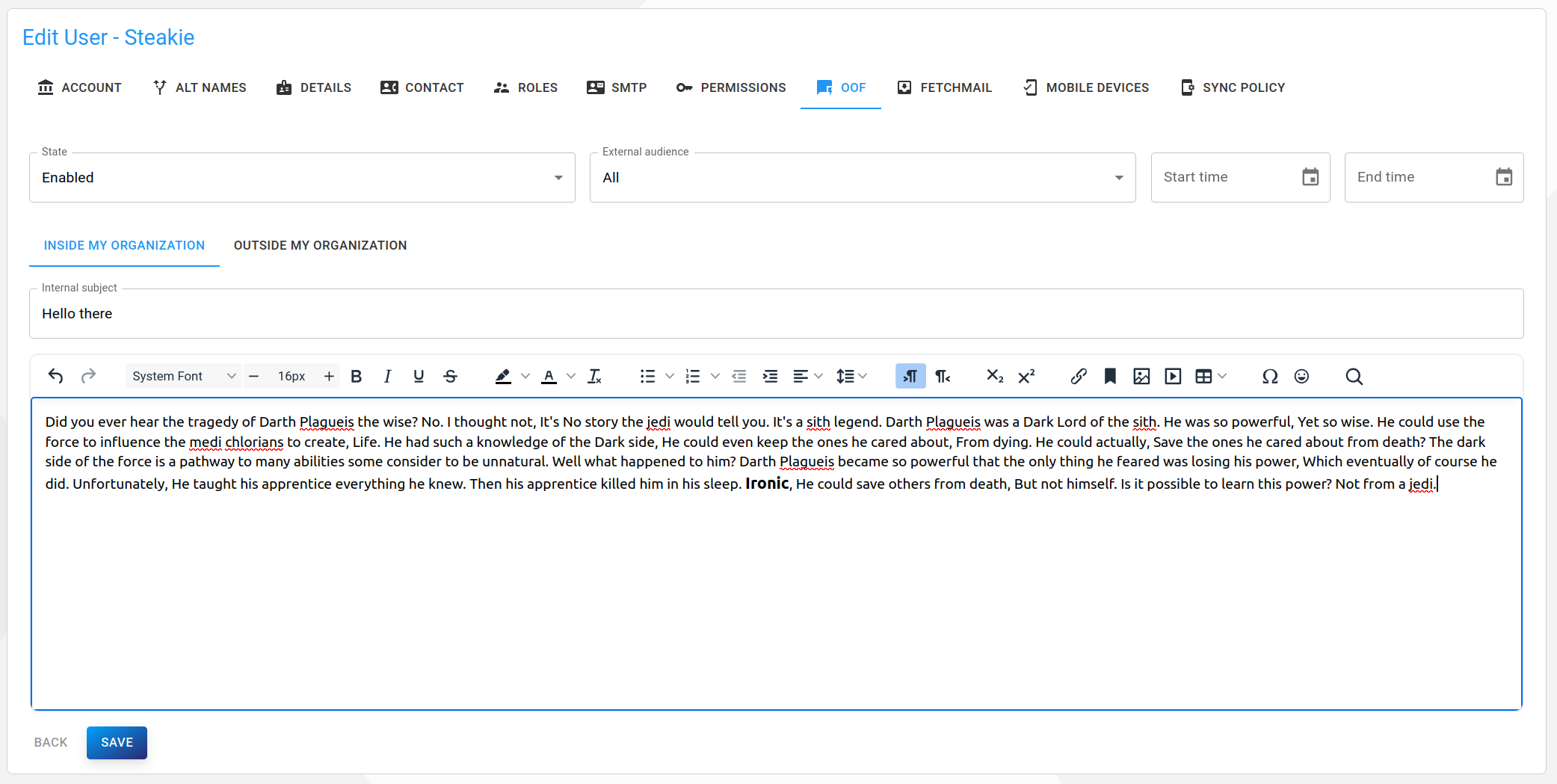
OOF
Out of office settings (auto-reply messages).
Fetchmail
It is possible to fetch e-mails from other mailserver via fetchmail. To configure this feature, you can add several e-mail servers and/or users to fetch mails from.
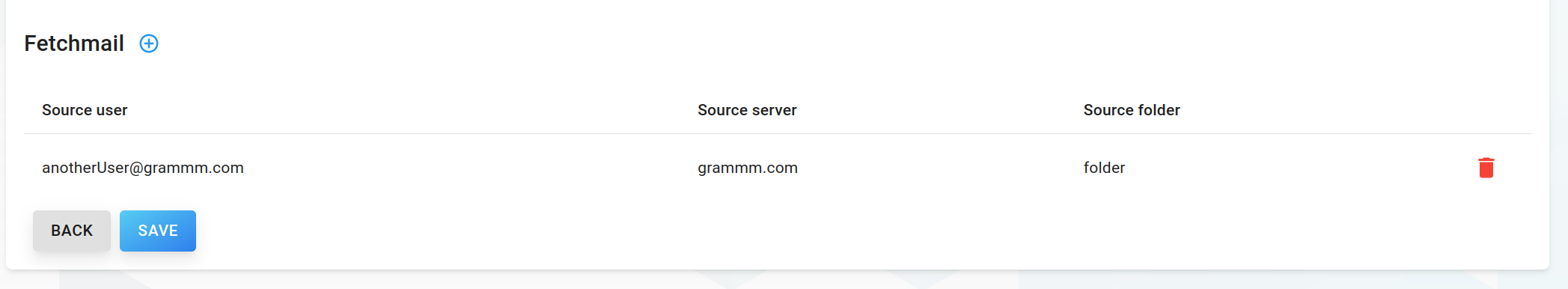
To add new fetchmail entry, click the circled plus icon, which will open the following input form:
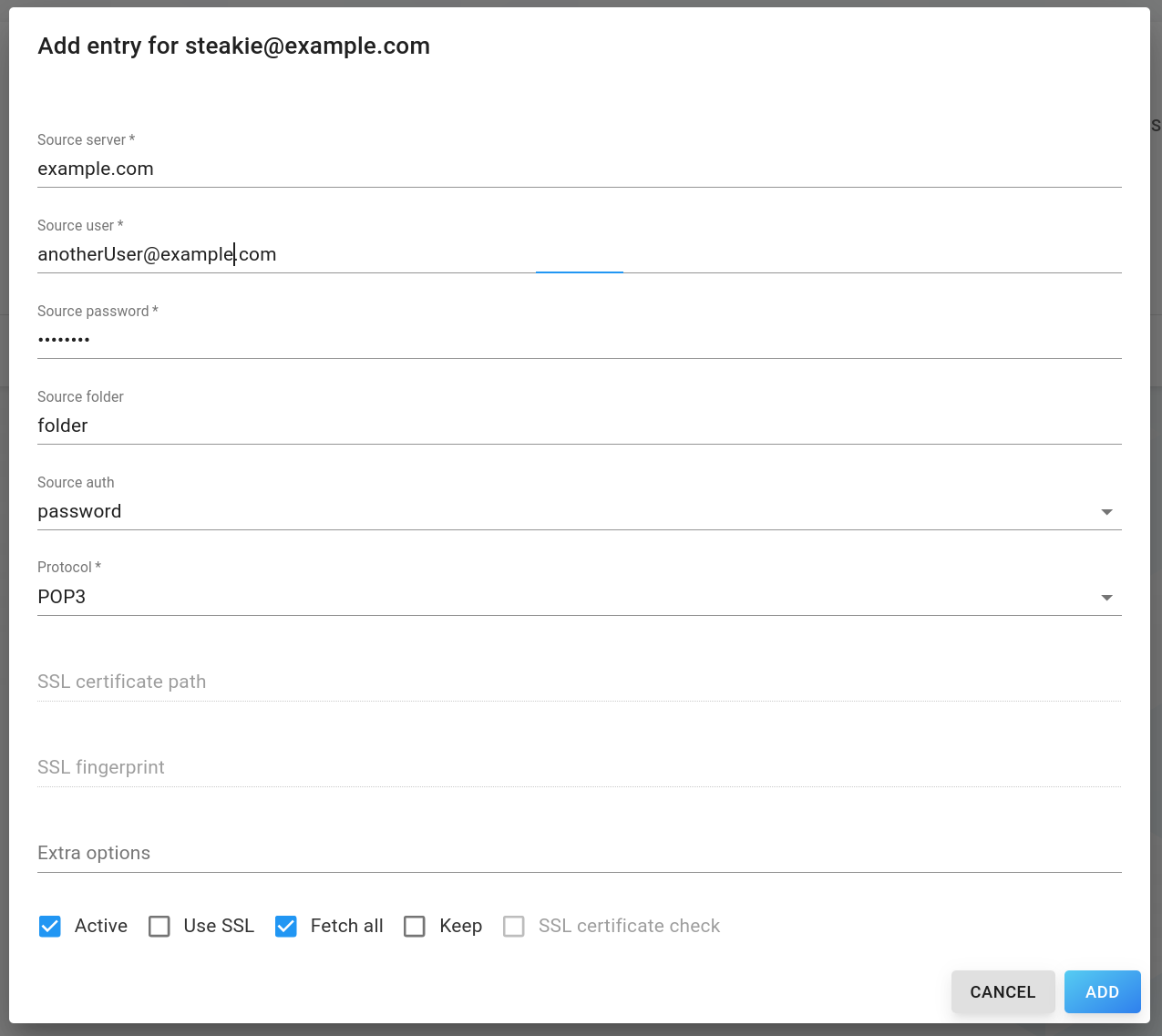
Source server (required): E-Mail server to fetch from
Source user (required): E-Mail address to fetch from
Source password (required): Password to the source users account (Hint: Single or double quotes are not supported)
Source folder (required): Source folder to sync from
Source auth: Type of authentication to use
Protocol (required): Protocol to use
SSL certificate path (if Use SSL is checked): Path to local certificate directory or empty to use local default
SSL fingerprint (if Use SSL is checked): Fingerprint of the server certificate
Extra options: (if Use SSL is checked): Additional fetchmail options
Active: Whether fetchmail is currently activated
Use SSL: Whether to use SSL
Fetch all: Whether to fetch seen mails
Keep: Keep original e-mails
SSL certificate check: Check ssl certificate
To edit these properties, click on a row in the table. To delete an entry, click the trash icon of a table row.
Important
Any changes will only be saved after clicking the click Save on the bottom of the page.
Mobile Devices
Synchronized mobile devices of this user
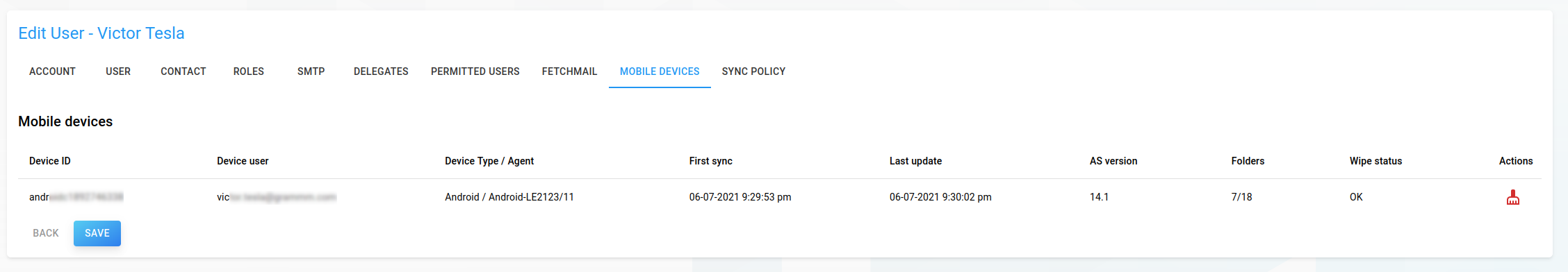
Actions:
Remote wipe: Engages a remote wipe for a device via MDM (Mobile Device Management)
Cancel remote wipe: Cancel above action
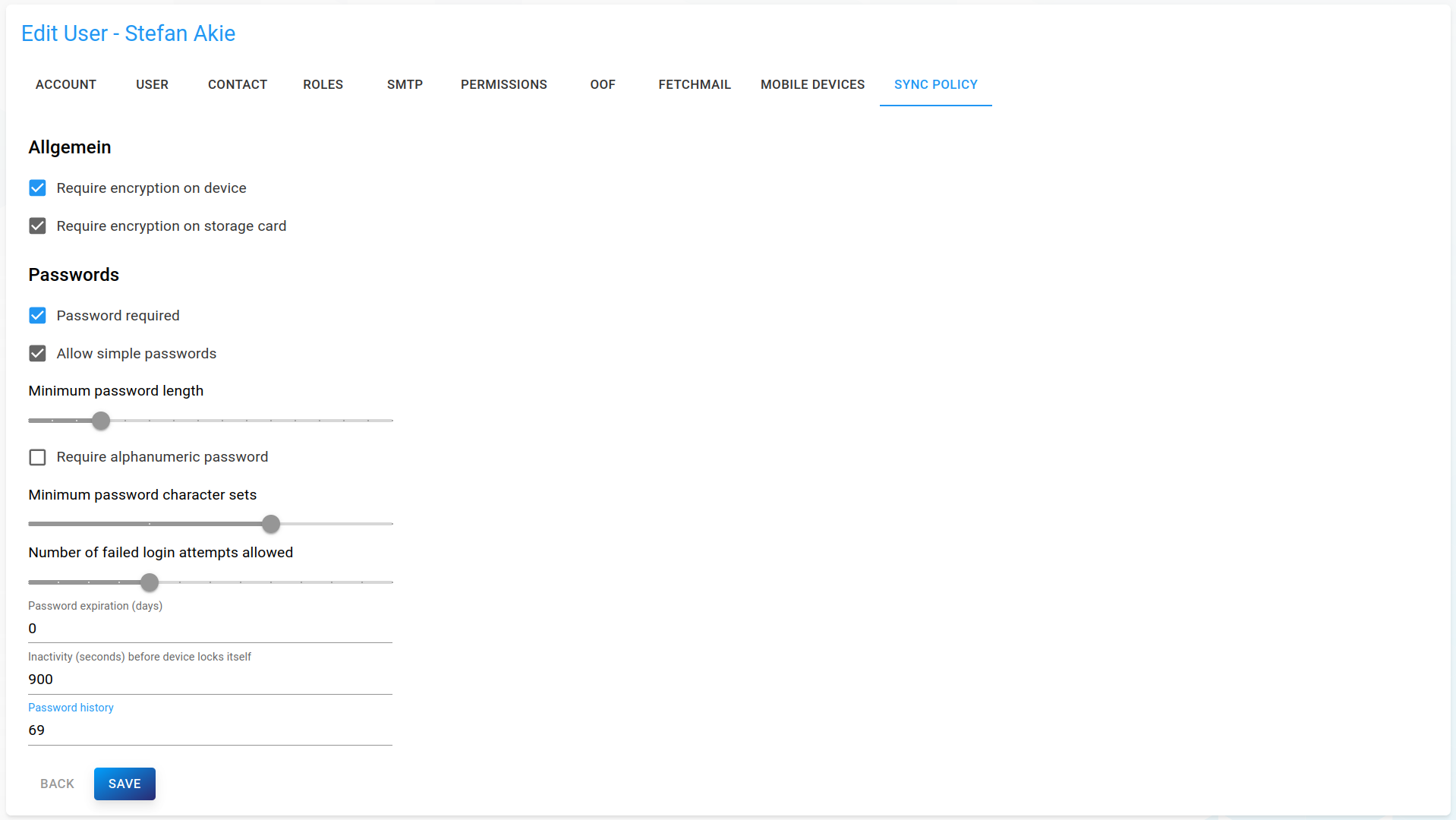
Sync policy
Specific MDM rules for this user. Unedited rules (greyed out) are adopted from the domain's policy.
Deleting a user
To delete a user, click on the trash icon of a user in the user view.
The following flags can be set:
Delete files: Will delete all files of this user
Click Confirm to confirm or Cancel to cancel.
Public folders
If at least one domain exists in the database, public folders can be added to a domain. To show existing public folders of a domain, navigate to the domain view in the drawer.
Click on a domain to expand available sub-pages and click on Public folders, which will redirect you to the list of folders of this domain. There are two views: A hierarchical view, like a common folder structure and a tree-like graph view.
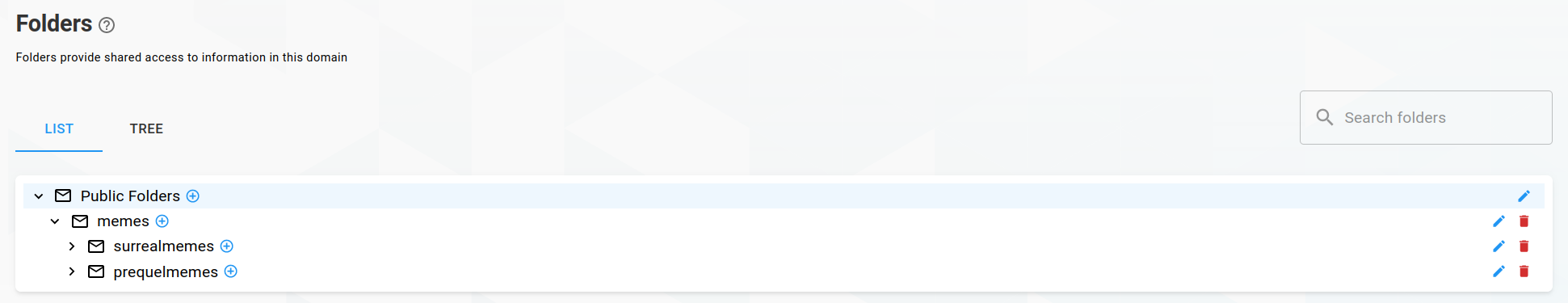

Adding a folder
To add a folder, click the Plus Circle icon of the folder's parent folder. Public Folders is the root folder, all other folders are put into. Thus the first folder is always within Public Folders (IPM_SUBTREE).
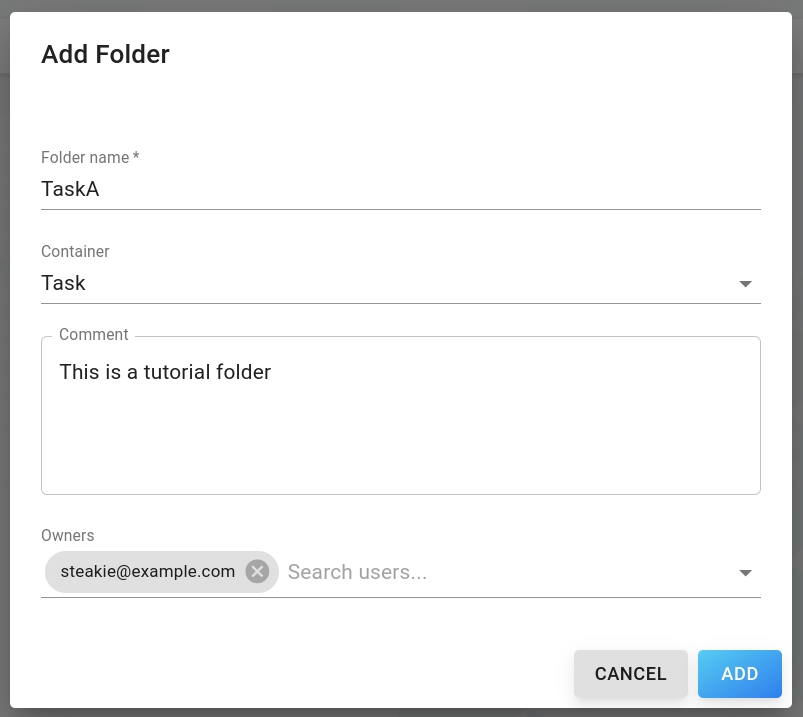
The following properties can be set:
Folder name (required): Name of folder
Container: Type of folder container
Comment: Comment
Owners: Owners of this folder (Multi-select of users in the database)
Click Add to confirm or Cancel to cancel.
Editing a folder
To edit an existing folder, click on the right Edit icon inside the hierarchy view to open the folder details.
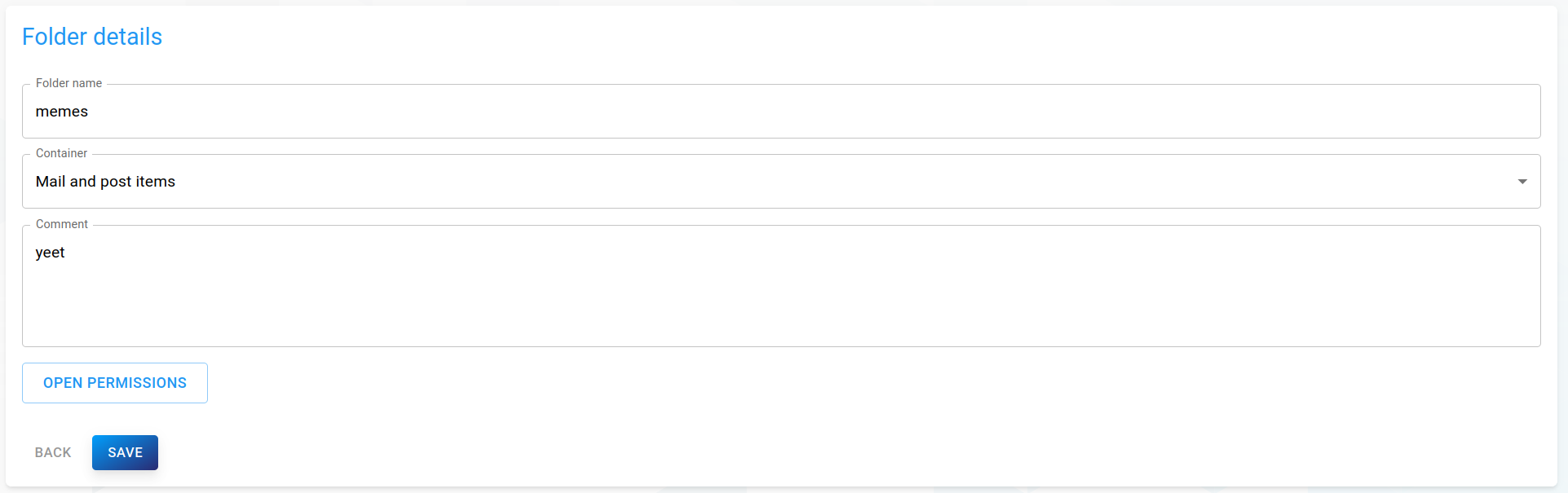
Simply change attributes to your needs, then click Save on the bottom to save your changes.
Folder permissions
To edit folder permission click on Open permissions to open the permissions dialog.
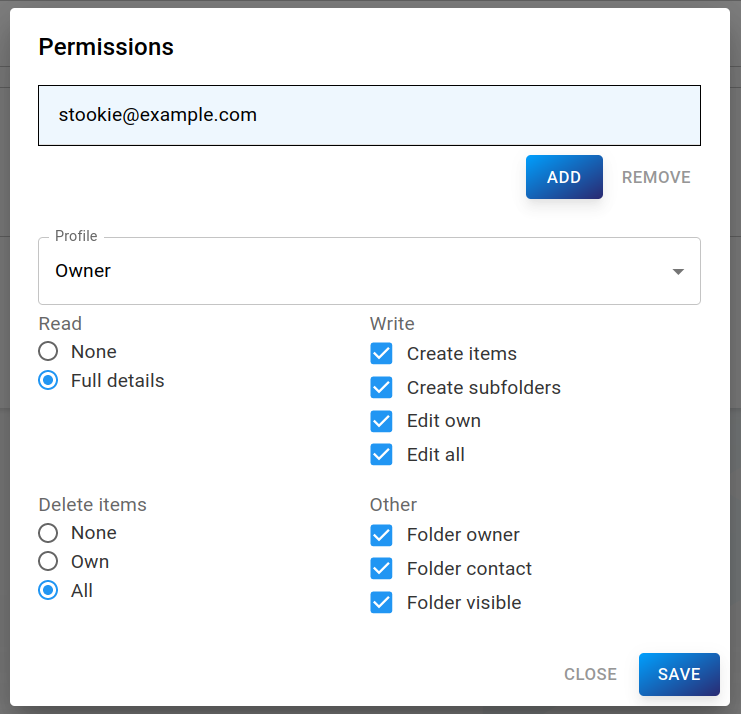
This form is a direct replica of grommunio-web's and outlook's folder permission settings. Select users to grant permissions at the top and set their permissions at the bottom.
Deleting a folder
To delete a folder, click on the trash icon of a folder in the folder view. Click Confirm to confirm or Cancel to cancel.
Groups
If at least one domain exists in the database, groups can be added to a domain. To show existing groups of a domain, navigate to the domain view in the drawer.
Click on a domain to expand available sub-pages and click on Groups, which will redirect you to the list of groups of this domain. If you have just installed grommunio or added the domain, the list will be empty.
Adding a group
To add a new group, click the blue NEW GROUP button to open the form dialog:
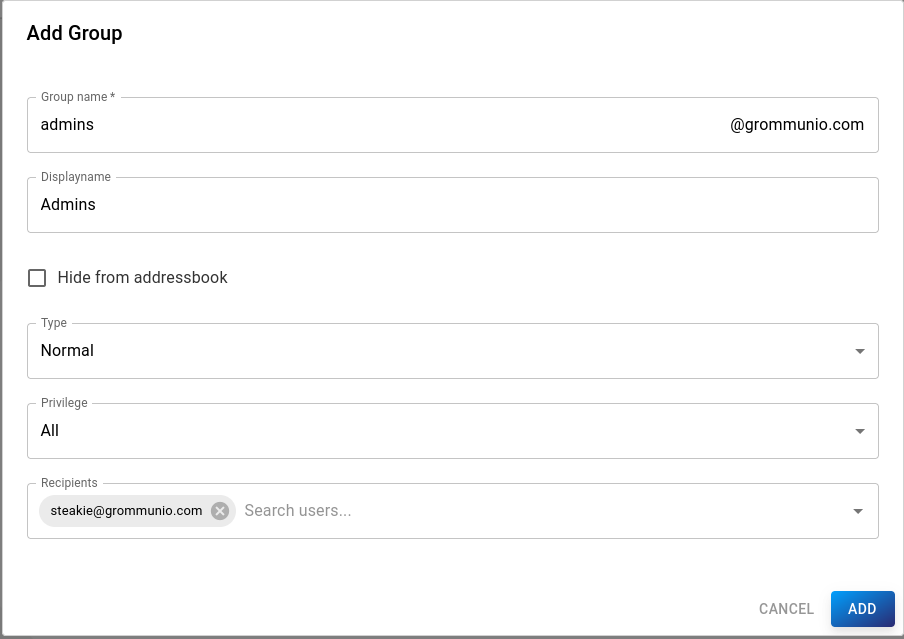
The following properties can be set:
Group name (required): E-Mail address of the group
Displayname: Displayed name of the group
Hide from addressbook: If selected, the mailing list won't be visible in the Global Address Book
- Type:
Normal: Select users as recipients
Domain: All users of the domain will be recipients
- Privilege: Users who are allowed to send E-Mails to the group
All: Everyone
Internal: All users of the group
Domain: All users in the domain
Specific: Specific users (Senders)
Recipients: Users of the domain, who are part of the group (not available if type=Domain)
Senders: Users, who are allowed to send e-mails to the group (only available if privilege=Specific)
Click Add to confirm or Cancel to cancel.
Deleting a group
To delete a group, click on the trash icon of a group in the list view. Click Confirm to confirm or Cancel to cancel.
Roles
Click on Roles in the drawer, which will redirect you to the list view of existing roles. If you have just set up grommunio, the table will be empty.
By default, every time a domain is added, a new role with rights for the new domain will be added. Additionally, you can create your own roles to specify access rights for multiple domains.
Adding a role
To add a new role, click the blue NEW ROLE button to open the form dialog:
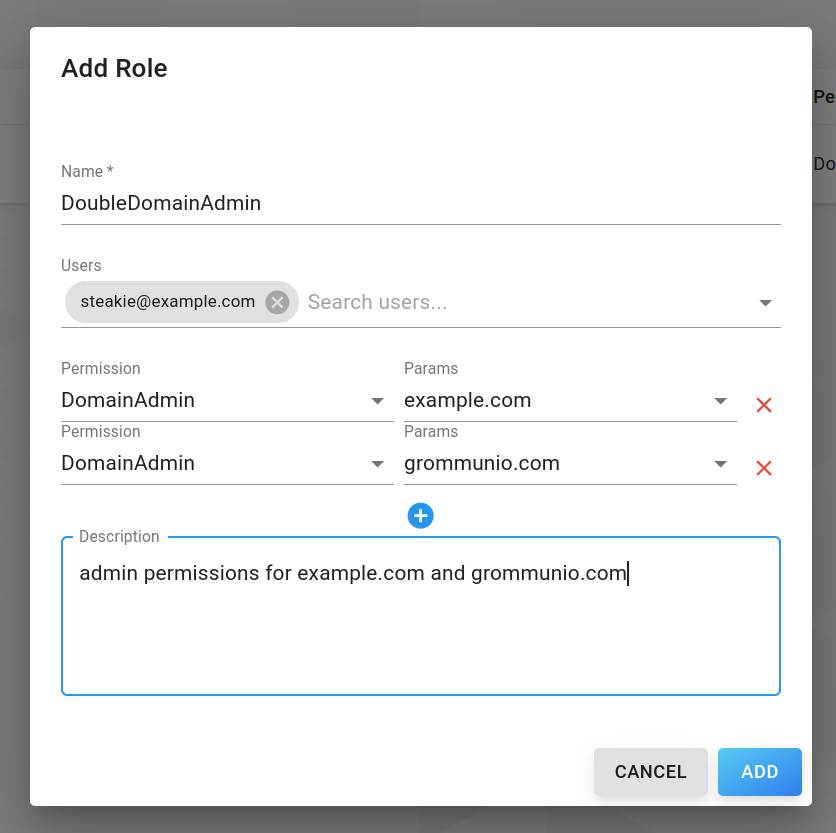
The following properties can be set:
Name (required): Name of the role
Users: Users to which this role will be assigned to
- Permissions:
SystemAdmin: Permits any operation
SystemAdminRO: Grants read-only permissions to system settings
DomainAdmin: Permits operations on for specific domain
DomainAdminRO: Grants read-only permissions to specific domain
DomainPurge: If present, grants permission to purge any writable domain
OrgAdmin: Grants DomainAdmin permission to any domain with matching orgID
Params: Domain/Organisation to get access to with this role
Description: Role description
Click Add to confirm or Cancel to cancel.
Editing a role
To edit an existing role, click on a role in the list to open the detailed view of a role.
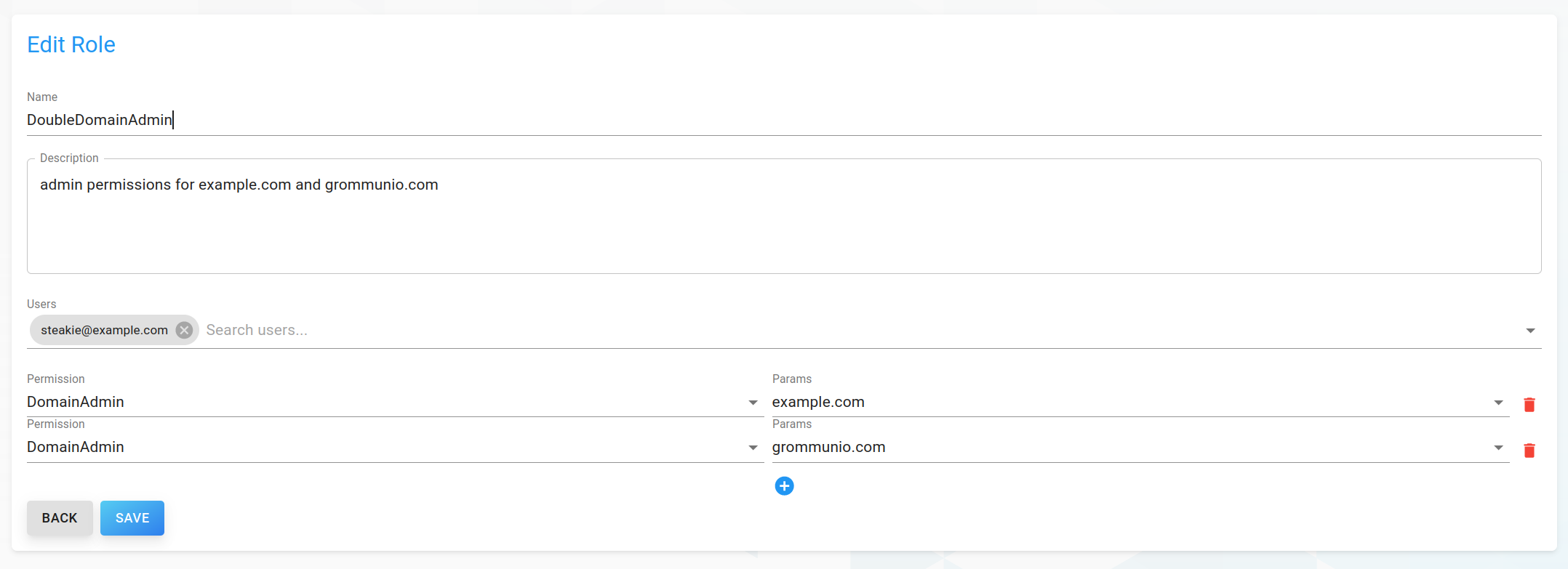
Simply change attributes to your needs, then click Save on the bottom to save your changes.
Deleting a role
To delete a role, click on the trash icon of a role in the list view. Click Confirm to confirm or Cancel to cancel.
Organizations
Click on Organizations in the drawer, which will redirect you to the list view of existing organizations. If you have just set up grommunio, the table will be empty.
Organizations are used to group domains, and give access to multiple domains in the system by using the OrgAdmin role. Every domain can be associated with at most one organization.
Adding an organization
To add a new organization, click the blue NEW ORGANIZATION button to open the form dialog:
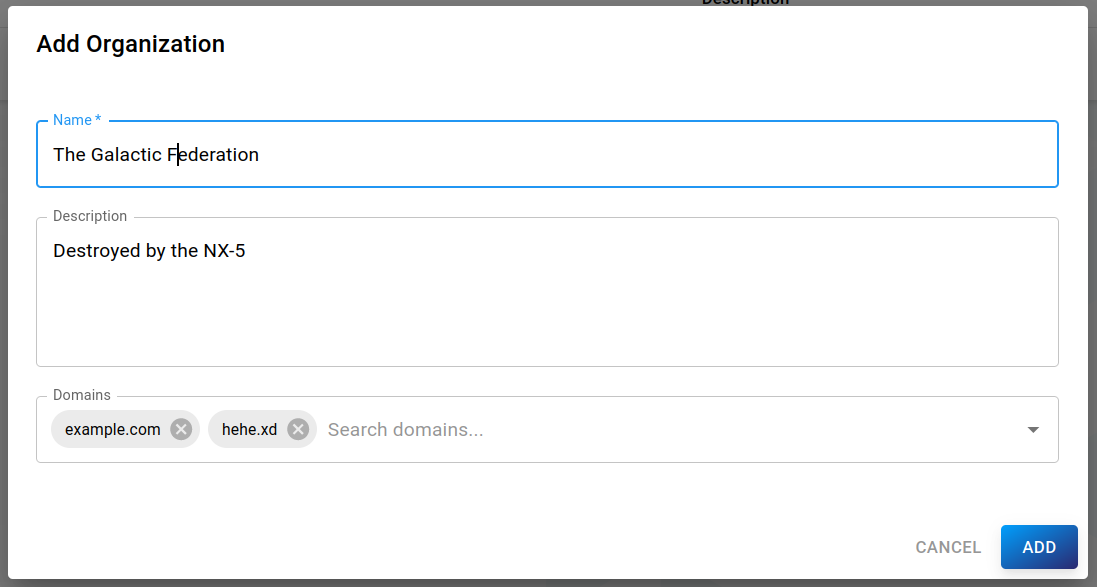
The following properties can be set:
Name (required): Name of the organization
Description: Detailed description of the organization
Domains: Domains which are part of this organization
Click Add to confirm or Cancel to cancel.
Editing an organization
To edit an existing organization, click on an organization in the list to open the detailed view of an organization.
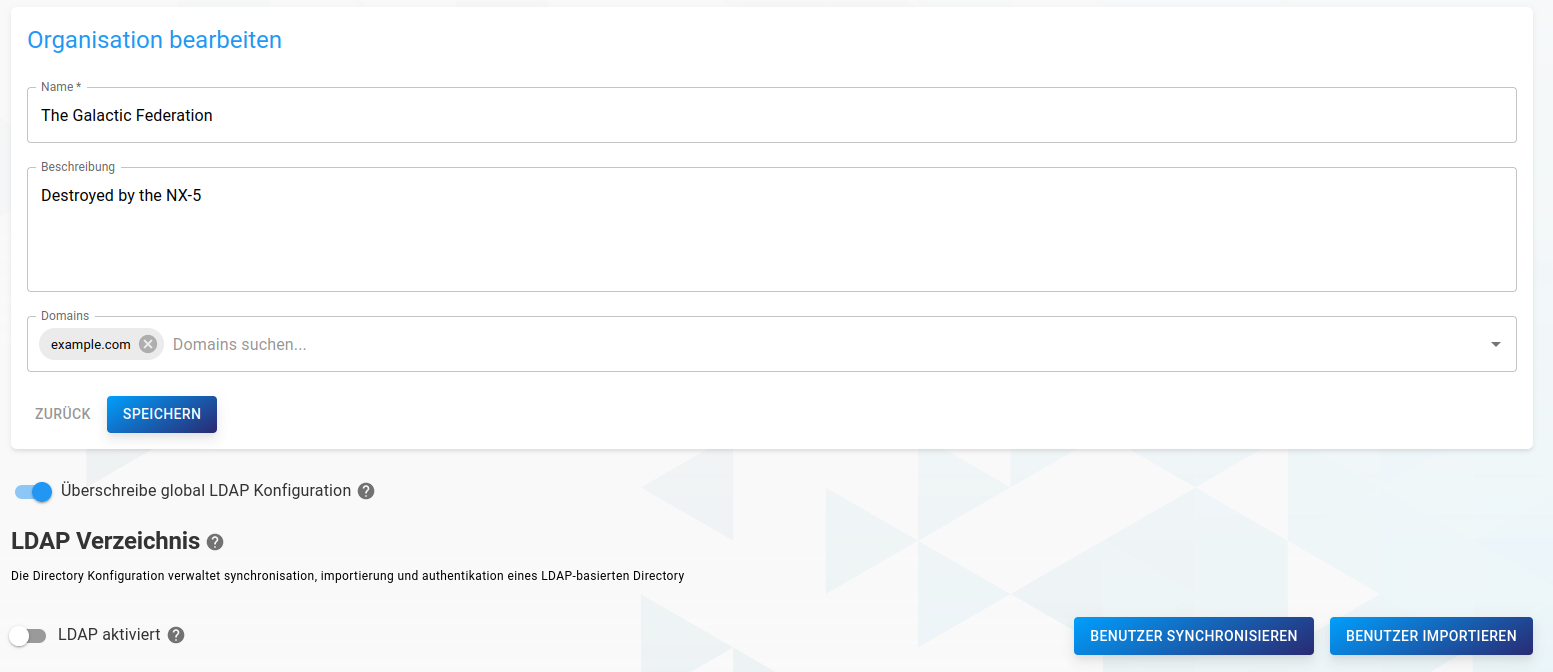
In this view, it is also possible to override the global LDAP configuration for domains in this organisation. To get more information about creating an LDAP config, see the LDAP section of this documentation.
Deleting an oranization
To delete an oranization, click on the trash icon of a role in the list view. Click Confirm to confirm or Cancel to cancel.
Defaults
To simplify the creation of domains and especially users, it is possible to set default create parameters. If set, the input masks for adding a domain or user will automatically be filled with these values.
Users with SystemAdmin permissions, can set global defaults by clicking on Defaults in the drawer.
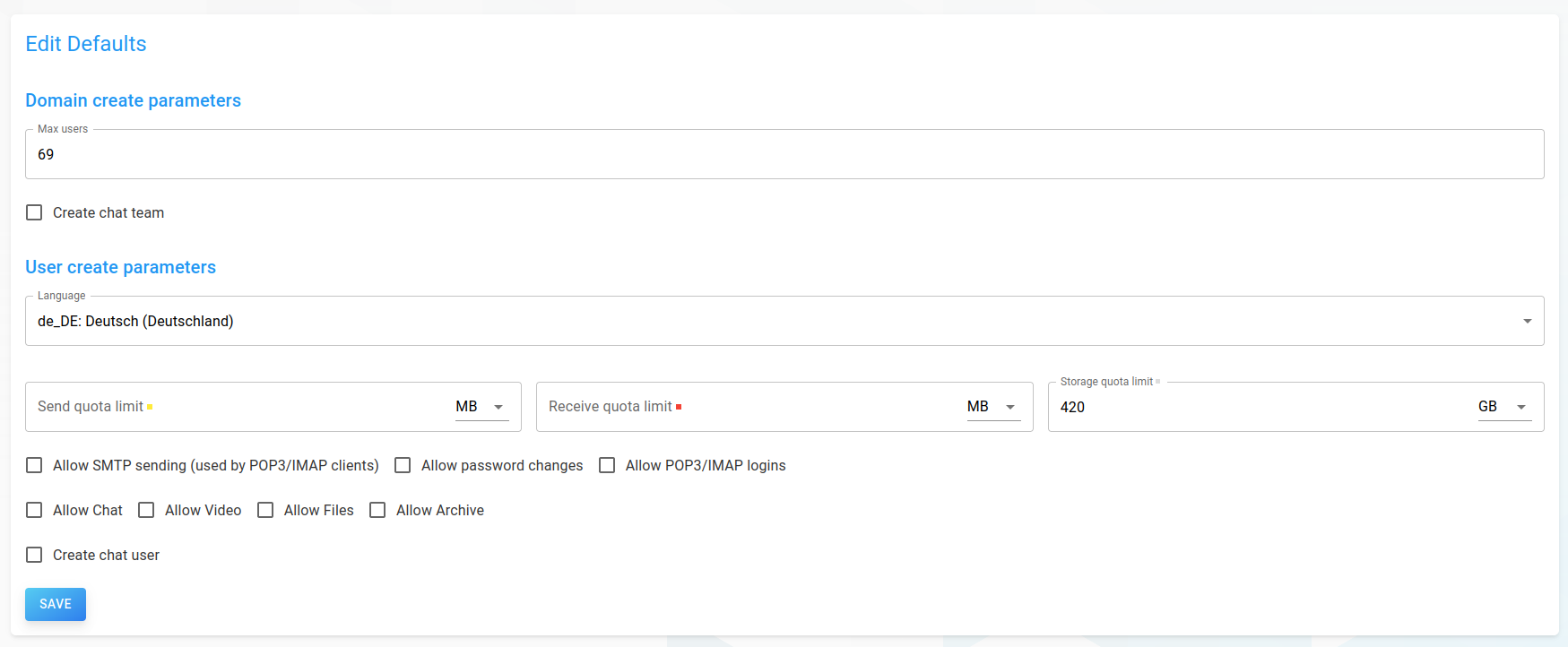
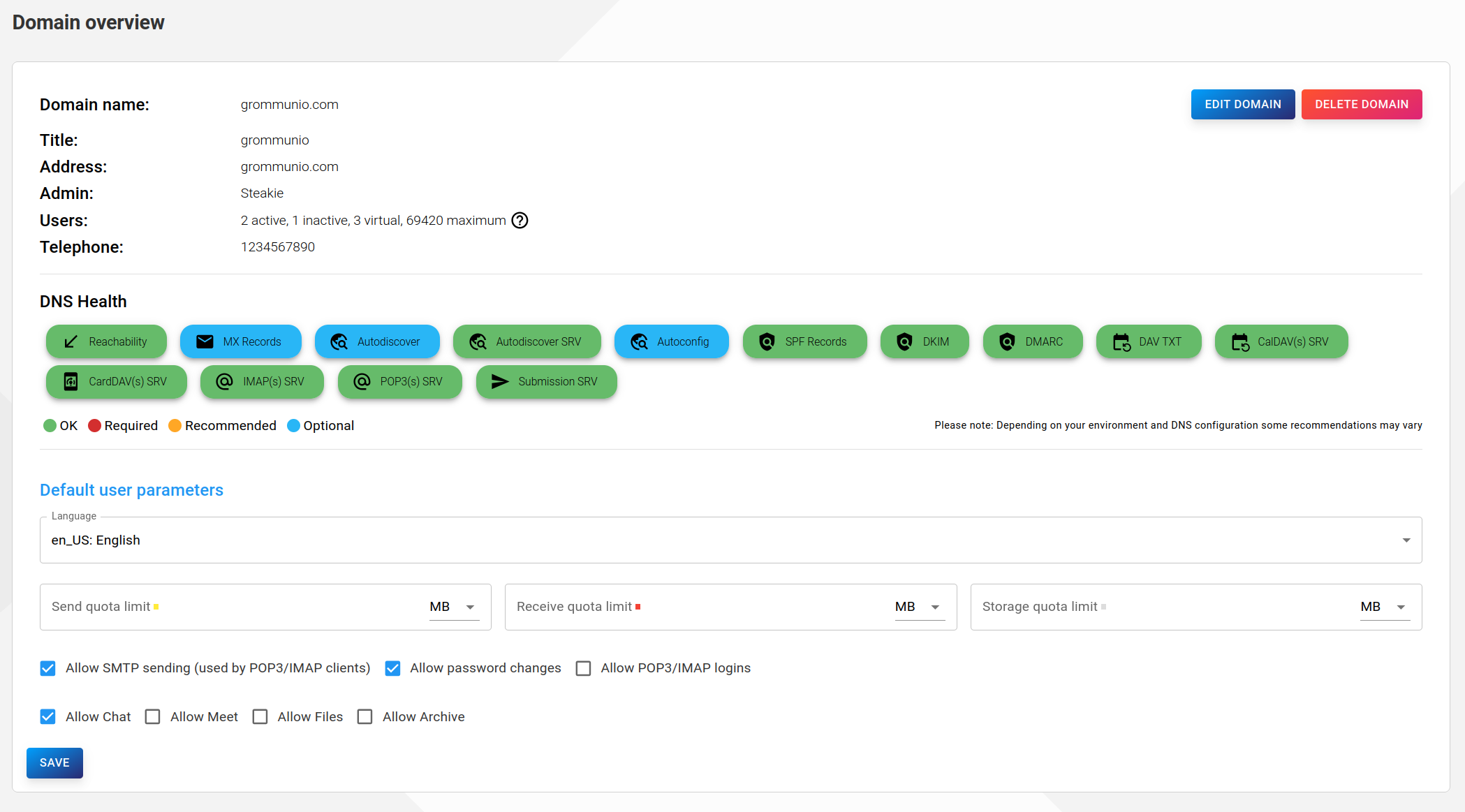
These values can be overwritten for each domain in the domain overviews:
Settings
Settings are split into server and user settings.
To change language, darkmode or theme, use the respective buttons in the topbar or the user icon
Server settings can be changed by clicking the settings icon in the topbar:

License
To use the full potential of grommunio you can upload your license by clicking Upload and selecting your purchased license. If you do not have a grommunio license yet, but want to upgrade, you can click on Buy now.
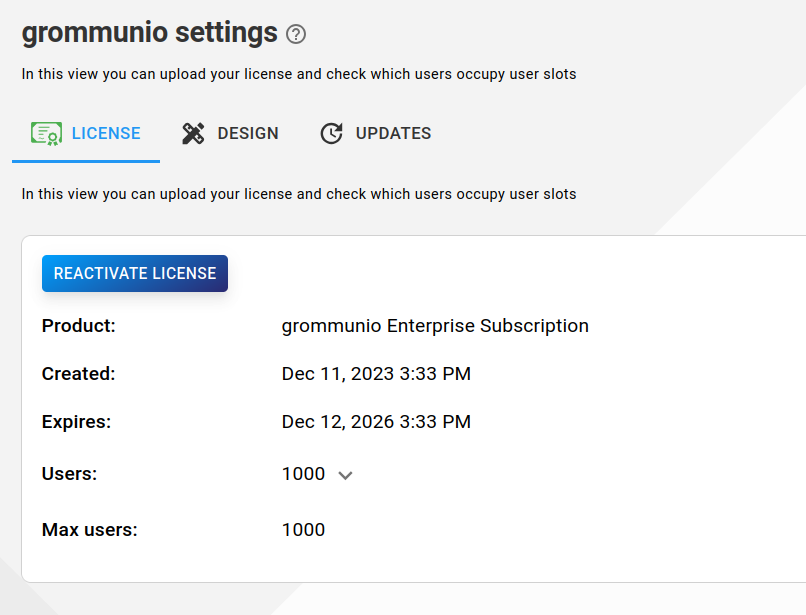
The following license properties are display:
Product: Type of grommunio subscription (Community, Business, etc...)
Created: Date on which the license was created
Expires: Last day on which the license needs to be renewed
Users: Current amount of users on this license
Max users: Maximum amount of users that can be created with the current license
If you click on the expansion icon next to the users count, you can see what users are occupying user slots of the license.
Design
Admins have the ability to whitelabel the grommunio-admin-web for all grommunio-admin-web users. There is a basic input mask, which helps you set custom app icons and background images.
It is possible to create separate sets of images for different hostnames. Click the plus icon to create a new set of images for a hostname. Following images can be set:
logo: The logo in the login formlogoLight: The logo in the expanded drawericon: The icon in the collapsed drawerbackground: The background image in light modebackgroundDark: The background image in dark mode
Each of these keys must be an URL to an image file.

As you can see, it is not necessary to overwrite every image, but the hostnames need to be accurate.
Click on the Show config button to display the customImages config object,
which needs to be copied into /etc/grommunio-admin-common/config.json on the server.
Application links
Links to external applications need to be configured in /etc/grommunio-admin-common/config.json on the server.
Following attributes are available:
rspamdWebAddress:String: Url of rspamd server (default:'')mailWebAddress:String: Url of mail webapp (e.g. grommunio-web) (default:'')chatWebAddress:String: Url of grommunio-chat (default:'')videoWebAddress:String: Url of grommunio-meet (default:'')fileWebAddress:String: Url of grommunio-files (default:'')archiveWebAddress:String: Url of grommunio-archive (default:'')
Additional server-side configuration
Following additional attributes can be configured at /etc/grommunio-admin-common/config.json on the server.
devMode:boolean: For development, enables redux logger (default:false)tokenRefreshInterval:int: Sets token refresh interval in seconds. (default:86400(24h))defaultDarkMode:boolean: Iftrue, the app will be set to dark mode, if not explicitly set by the user/browser (default:false)defaultTheme:string: Name of the default theme to use. Available themes: grommunio, green, purple, magenta, teal, orange, brown, bluegrey (default:"grommunio")loadAntispamData:boolean: Whether or not to load antispam data in the dashboard (default:true)searchAttributes:Array<String>: Array of strings, possible LDAP Search attributes (default: All attributes)
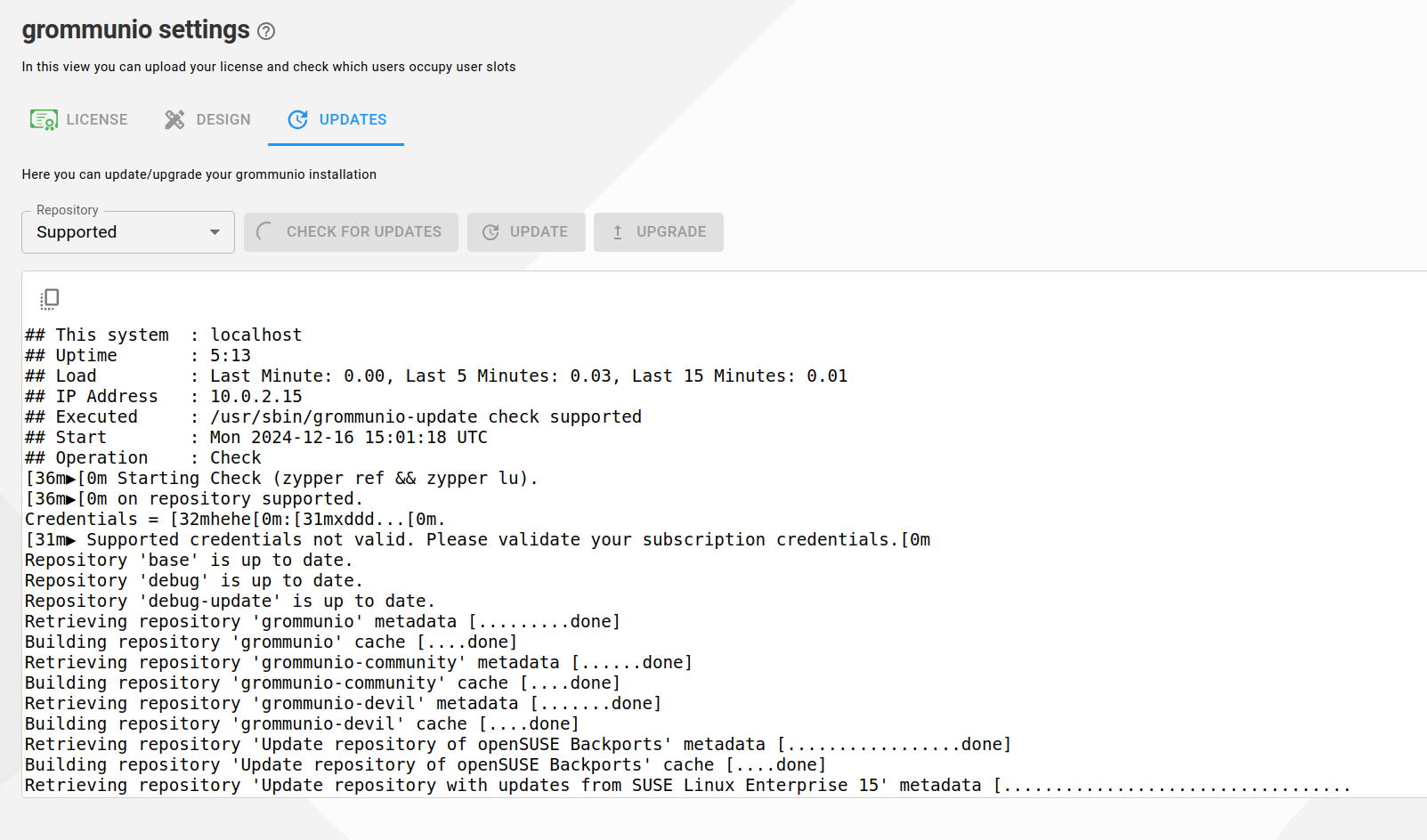
Updates
It is possible to update and upgrade server packages within grommunio-admin-web.
Choose repository: Community (publicly available) or Supported (license required)
Check for updates, update or upgrade packages by clicking the respective buttons
LDAP
It it possible to synchronise users from external user directories using LDAP. To configure LDAP, click on LDAP in the drawer, which will redirect you to the LDAP form to define a global LDAP configuration. This config can be overwritten for each individual organisation. To do so, navigate to Organisations and open the detailed view of an organisation. Flip the Override global LDAP config switch and set a config according to the following specification.
Important
Please note that configuration changes are not automatically applied to the services already running. Make sure to restart the services to be able to pick up the LDAP authentication first.
After applying a new LDAP configuration, the services are intentionally not automatically restarted as this would result into possibly inconvenient downtime if existing internal users are already used by the authentication manager (authmgr). Services can either be restarted through admin UI in the dashboard section or via systemd directly:
systemctl restart gromox-{http,zcore,pop3,delivery,delivery-queue,midb,imap}
Availability
LDAP not available means the LDAP config isn't set up correctly or the server can't be reached. If you want to disable LDAP manually, flip the LDAP enabled switch.

Configuration
Through this form, you create a ldap.yaml file, which configures an LDAP connection.
Properties are split into the following categories:
LDAP Server
Attribute Configuration
Custom Mapping
To save a configuration, click Save at the bottom or click Delete Config to delete the current configuration.
LDAP Server
The following properties are available:
LDAP Server (server): Address of the LDAP server to connect to
LDAP Bind User (bindUser): DN of the user to perform initial bind with
StartTLS: Whether to utilize the StartTLS mechanism to secure the connection
LDAP Base DN (baseDn): Base DN to use for user search
Authentication manager
Primary authentication mechanism
Always MySQL (default): MySQL authentication
Always LDAP: LDAP authentication
Automatic: The choice between LDAP/MySQL occurs dynamically, depending on whether the user was imported from LDAP originally.
Attribute Configuration
The following properties are available:
LDAP Templates (templates): Template to prefill any fields below. Available are:
OpenLDAP
ActiveDirectory
LDAP Filter (filters): LDAP search filter to apply to user lookup
Unique Identifier Attribute (objectID): Name of an attribute that uniquely identifies an LDAP object
LDAP Username Attribute (username): Name of the attribute that corresponds to the username (e-mail address)
LDAP Default Quota (defaultQuota): Storage quota of imported users if no mapping exists
LDAP Display Name Attribute (displayName): Name of the attribute that contains the name
LDAP Search Attributes
Controls which attributes the "Search in LDAP" functionality will look at when searching using an arbitrary search string.
Custom Mapping
LDAP attribute -> PropTag mapping to use for LDAP import. Any mappings specified take precedence over active templates.
You can create a list of (Name, Value) pairs
Name: Name of the PropTag the attribute maps to
Value: Value of the PropTag the attribute maps to
User import and synchronisation
To import/sync users from all domains, you have to have SystemAdmin permissions. If you do, click on IMPORT USERS or SYNC USERS. This will import/sync all users of all domains.
If you don't have these permissions, you can import/sync users for your domain. To do that, navigate to the user list(s) of your domain(s).
Importing users will synchronise all already imported users and also import new ones. Synchronising will only do the first.
Domain user import and synchronisation
In the users list, you can either import/sync all users of this domain by clicking Import/Sync ldap users. If you want to import specific users, you can do the following:
User import
Click on Search in ldap to open a list view of ldap users. Simply enter a username at the searchbar and click the import icon of a user to import.
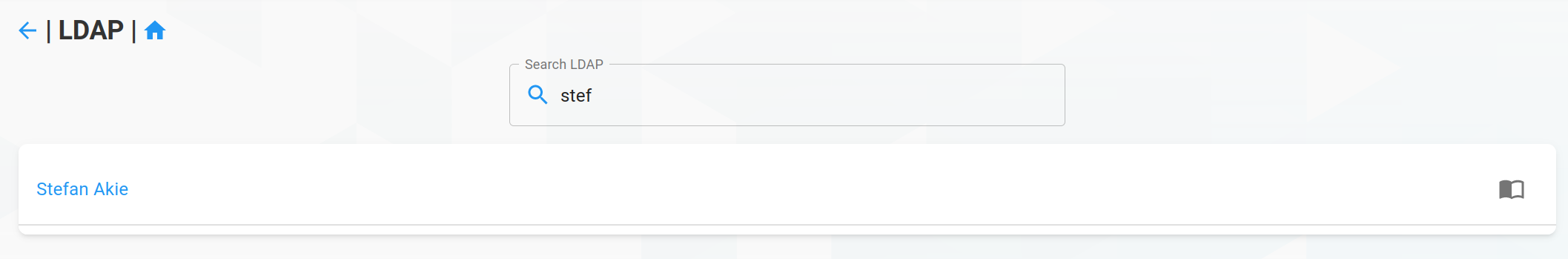
There is the option to force the import. If checked, an existing user with this usename in the grommunio database will be overwritten.

You can sync these specific users by clicking on them in the list view and clicking the Sync button in the detailed view (only for LDAP users).
Detaching a user
If you want to modify an ldap user, you need to detach it from ldap. You can achieve this by clicking Detach in the detailed user view. This essentially removes the synchronisation until forcefully overwriting the user via another import.
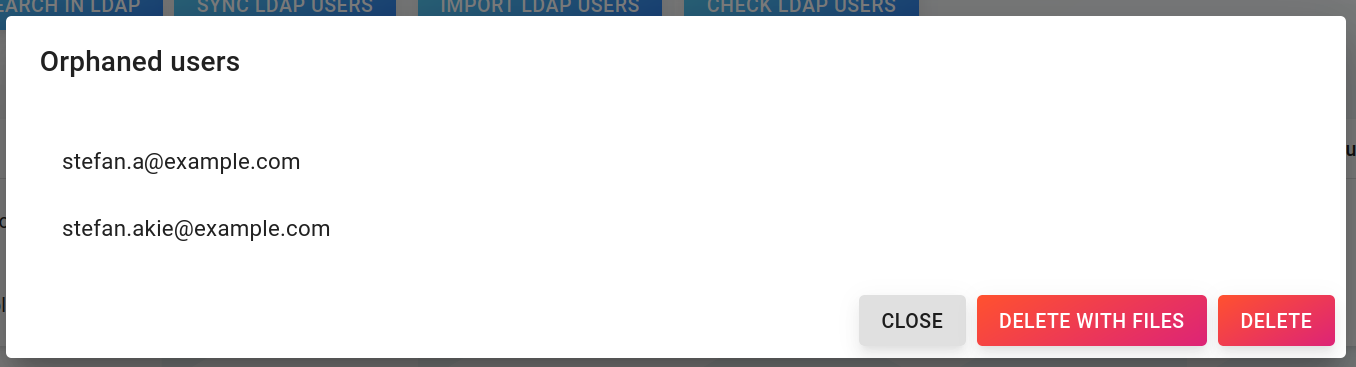
Removing orphaned users
If a user was removed from the ldap directory, the imported user will be orphaned. To show and/or delete currently orphaned users, click on Check ldap users.
DB Configuration
It is possible to create config files in the database to manage services. Every config file manages exactly one file and includes lines of (key, value) pairs.
This creates a hierarchical structure:
- ServiceA
- FileA
foo=bar
- FileB
test=example
test2=example2
- ServiceB
- FileC
key=value
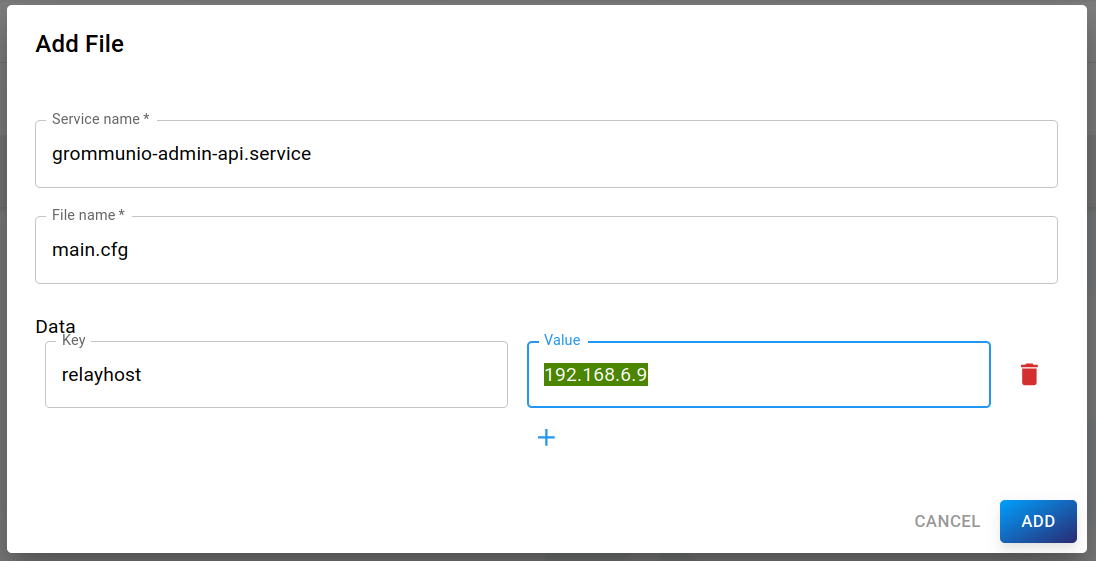
Adding a file
A useful example would be to configure a relayhost in postfix:
Editing a file
To edit a file, click on the service the file belongs to. This will open a detailed view of the service with a list of its files. Click on a file to open its detailed view and edit the (key, value) pairs to your needs.
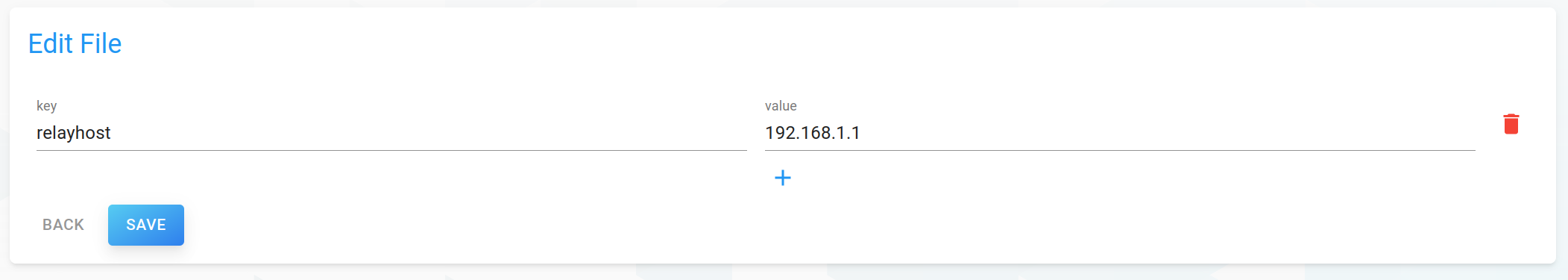
Click Save to confirm or Cancel to discard your changes.
Deleting a file
To delete a file, click on the service the file belongs to. This will open a detailed view of the service with a list of its files. Click on the trash icon of a file to delete it and confirm.
Configuring grommunio-dbconf
grommunio-dbconf is an internal service, that will execute actions/commands when configs change. These actions can be specified for every service separately.
Adding a grommunio-dbconf file
Actions to be executed when a config of a service <servicename> changes, need to be set in the file grommunio-dbconf/<servicename>.
There are pre-made commands to set for either key, file or service changes. Those can be found on the Commands tab.
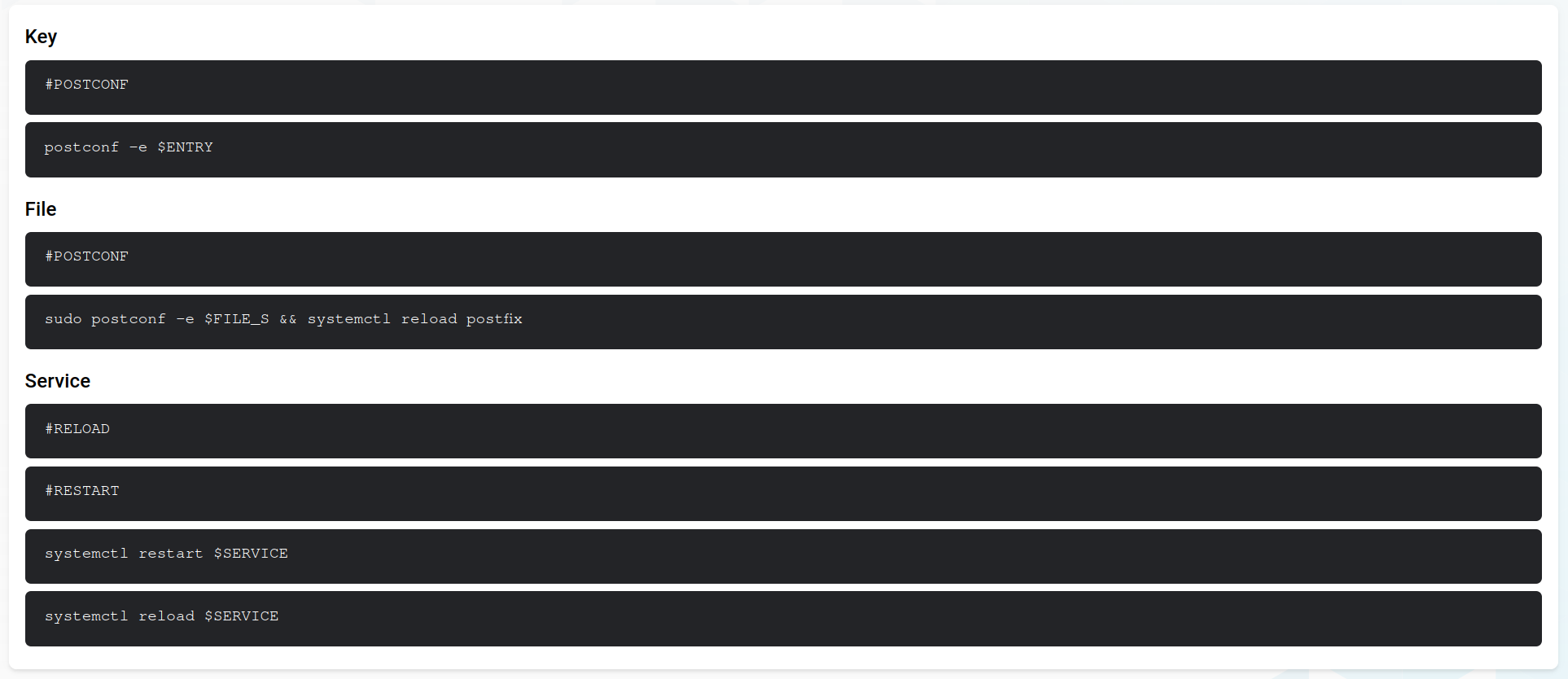
If a command doesn't exist, the next lower level command will be executed (service -> file -> key).
For example, you could configure postfix changes like this:
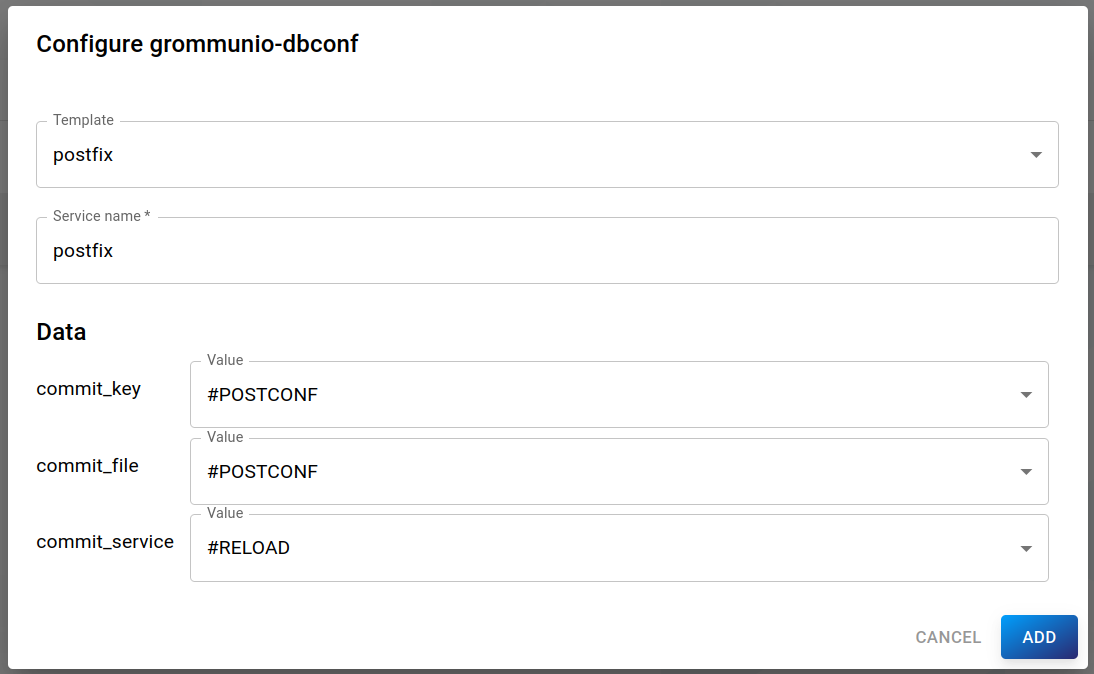
This will, among else, restart the service if the service config changes.
Servers
If grommunio is running on a distributed system, the list of servers can be added in this view. It is possible to specify the selection policy for user distribution. You can select from:
round-robin: Always use the server on which a user has not been added for the longest time (in a circle-like manner).
balanced: Put new user on server with least workload
first: Always use the first server
last: Always use the last server
random: Pick a random server
Adding a server
To add a new server, click the blue NEW SERVER button to open the form dialog:
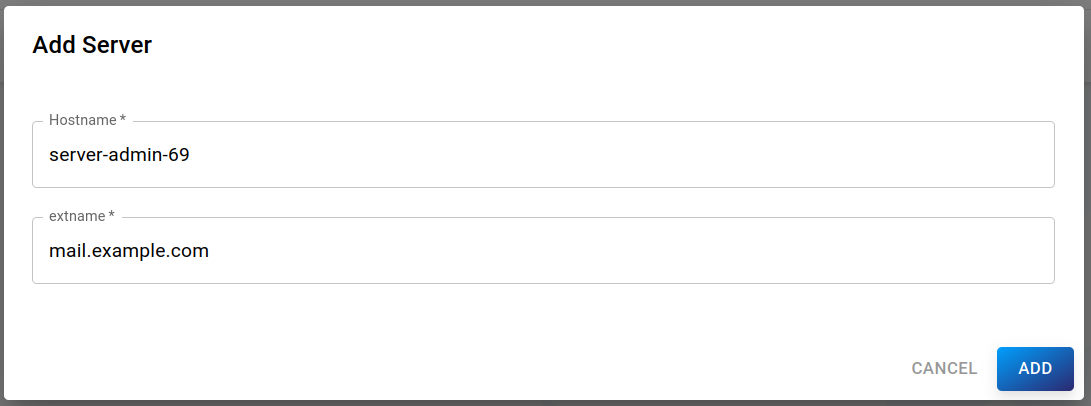
The following properties can be set:
Hostname (required): Internal server hostname
Extname (required): Hostname for external access (DNS-Name)
Editing a server
To edit an existing server, click on a server in the list to open the detailed view.
Simply change attributes to your needs, then click Save on the bottom to save your changes.
Logs
Click on Logs in the drawer, which will redirect you to the list of available logs. Usually, you will see a list of grommunio/gromox services, which journalctl logs you can view here.
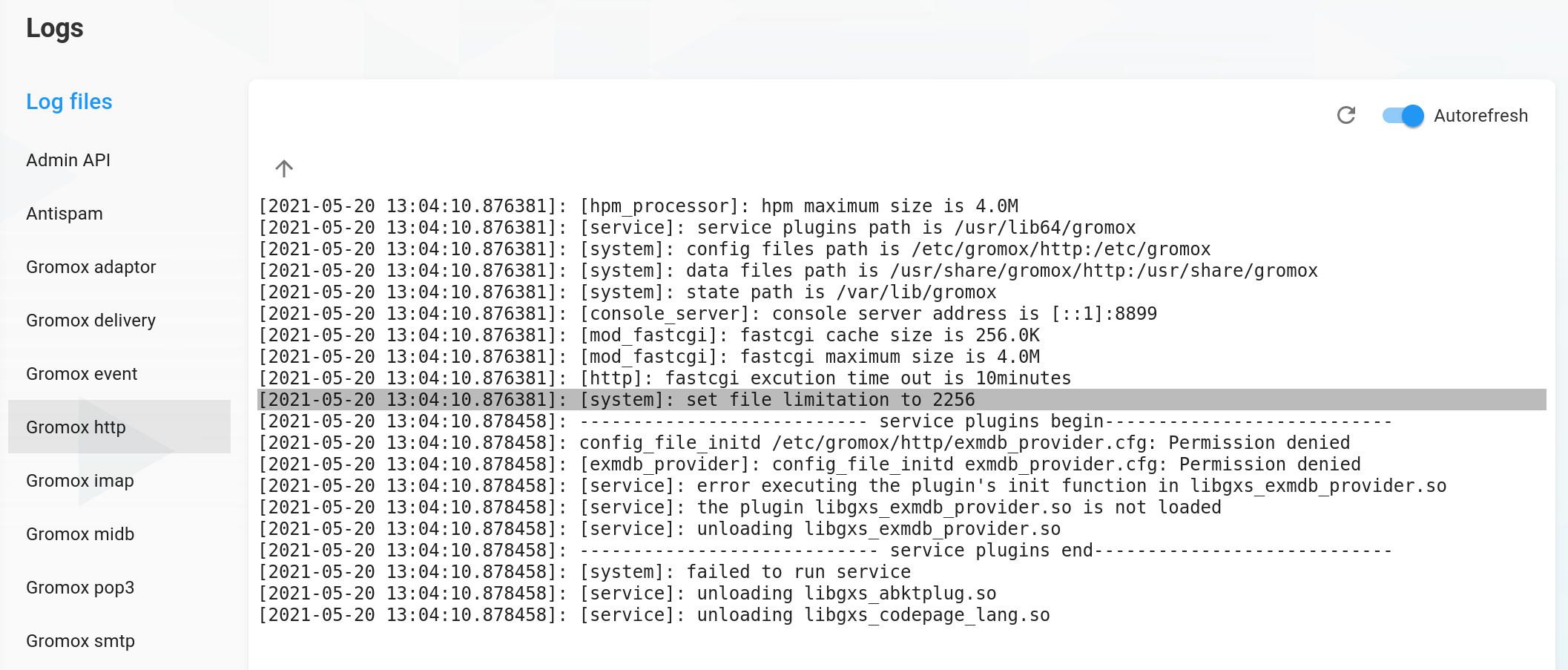
Click on the uparrow to show previous logs. Click on the the refresh button to fetch new logs or toggle the autorefresh switch to automatically refresh logs of the selected service every 5 seconds. Click on a log line to fetch every log after the timestamp of the clicked line.
Mail queue
Click on Mail queue in the drawer, which will redirect you to the view of the current postfix and gromox mail queue.
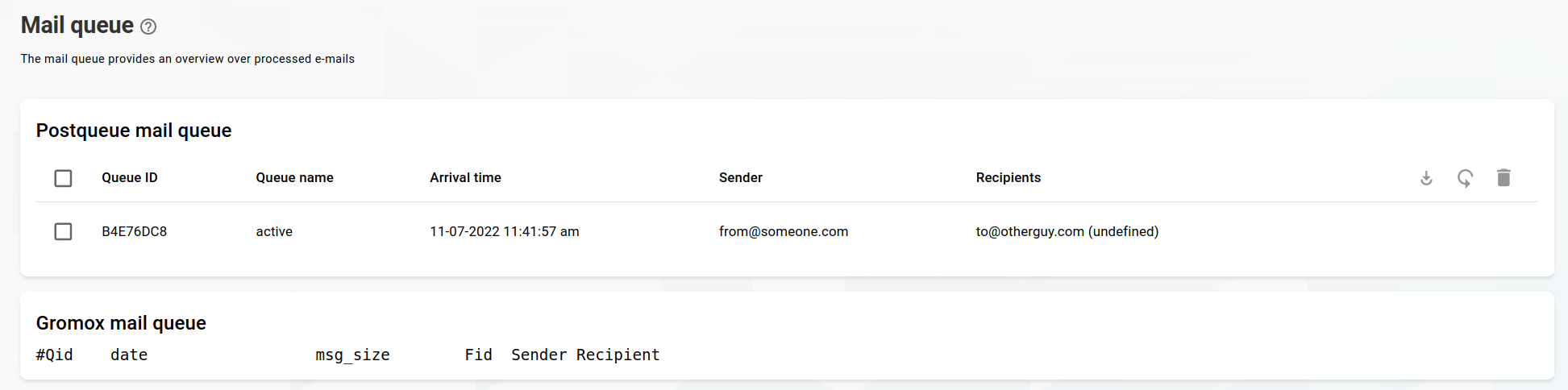
These lists will update automatically every 10 seconds.
Actions
Select table rows by clicking the checkboxes. Mail queue actions will be used on the selected entries.
The actions are:
Flush: Try to continue mail processing
Requeue: Remove mail from queue and add queue the same mail as new entry
Delete: Permanently remove mail from queue
Tasks
Click on Mail queue in the drawer, which will redirect you to the Tasks view.
Tasks are created for operations which could potentially take a long time. Currently, this includes LDAP sync and folder deletion. If one of these operations take too long, a background task is created, which can be viewed in this table.
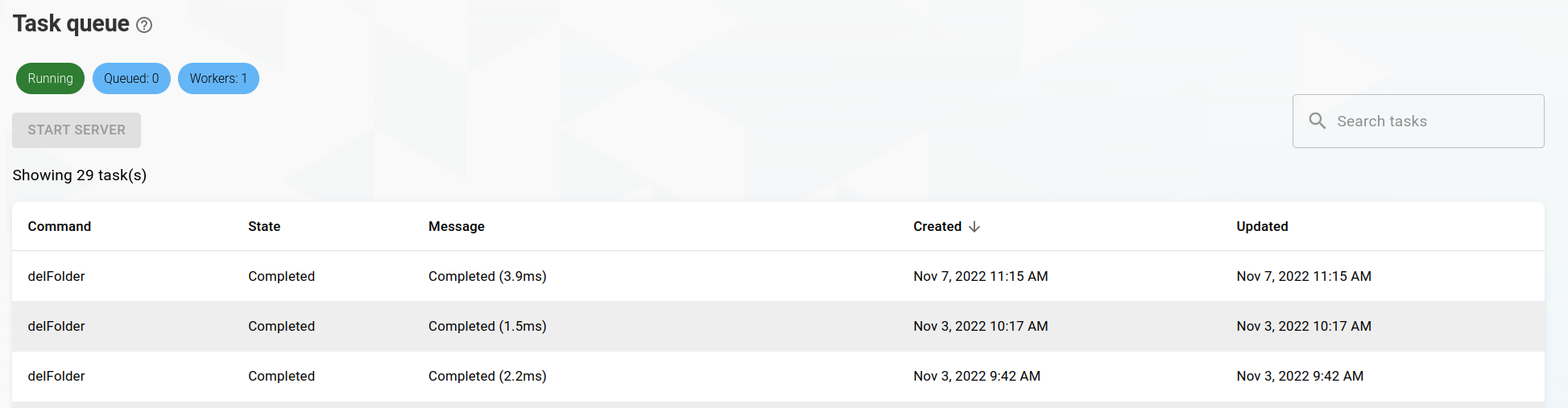
In case the internal task processor is not running, it can be started manually by clicking the Start server button.
Further task details can be seen in the task details view, by clicking on a task in the table.
Mobile devices
Click on Mobile devices in the drawer, which will redirect you to the list of synchronised mobile devices. This view is a recreation of the grommunio-sync-top CUI.
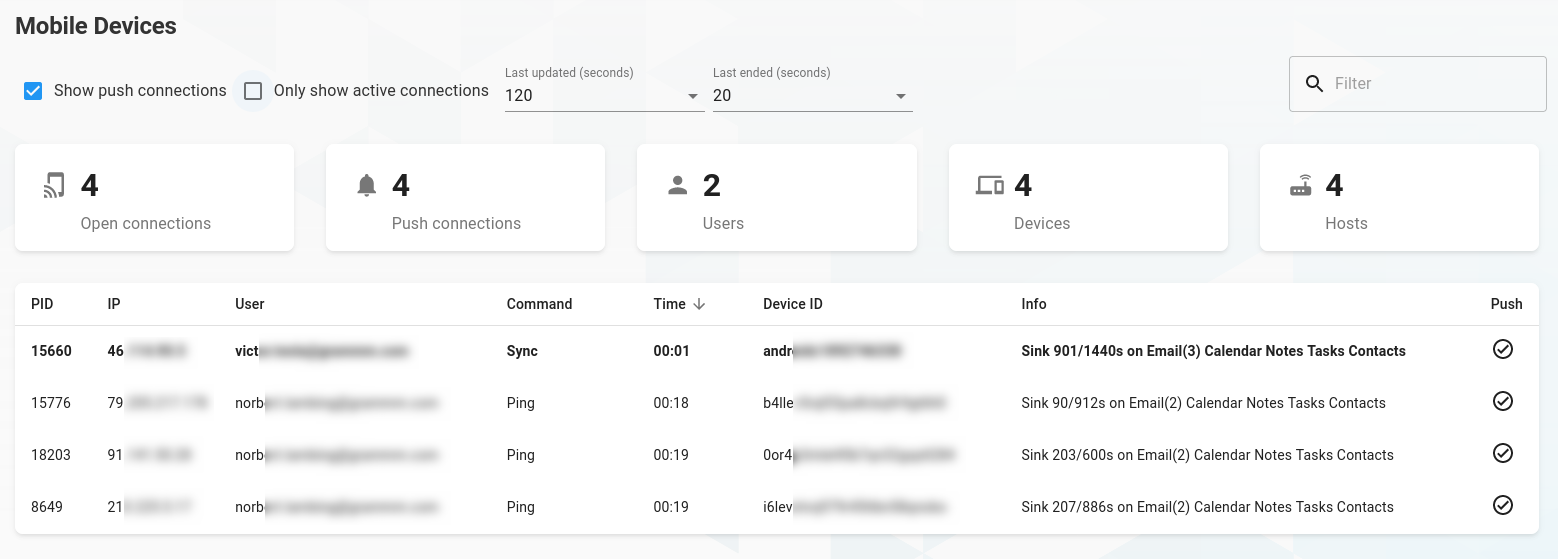
The view will update the devices every 2 seconds. On the top, you can specify filters for the table, like text-based search or activity of devices.
Sync policies
The synchronisation behavior of devices is specified by the sync policies, which are a set of rules. When a user logs into an account, these policies will be applied to the device and updated as soon as the policy is changed. It is not possible to change the policies globally, but per domain (all users of a domain) or per user. To change the policy for all users of a domain, navigate to the list of domains and click on the domain for which you want to change the policy. Under the Sync policy tab, you can see the current rules.
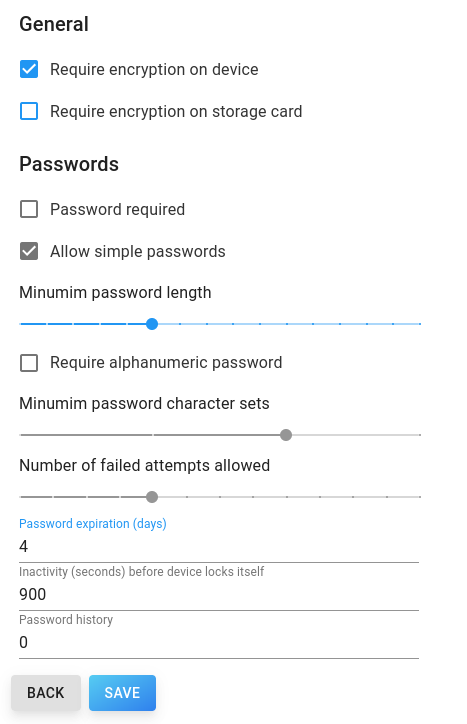
Blue checkboxes, sliders or textfields indicate deviations from the default policy, grey ones match it.
To specify specific rules for a user, navigate to list of users and click on the user for whom you want to change the policy. Just like domain-specific policies, current rules are displayed under the Sync policy tab. Again, blue checkboxes, sliders or textfields indicate deviations from the domain policy of this user, grey ones match it.
Live Status
Click on Live Status in the drawer, which will redirect you to the live, realtime view of the grommunio web services. Any HTTP request shows up in live status, including MAPI/HTTP, EAS, EWS and other requests made. All connections other than grommunio Groupware, e.g. Chat and Files are also viewable and can be tracked by the entrypoint URL in the list.
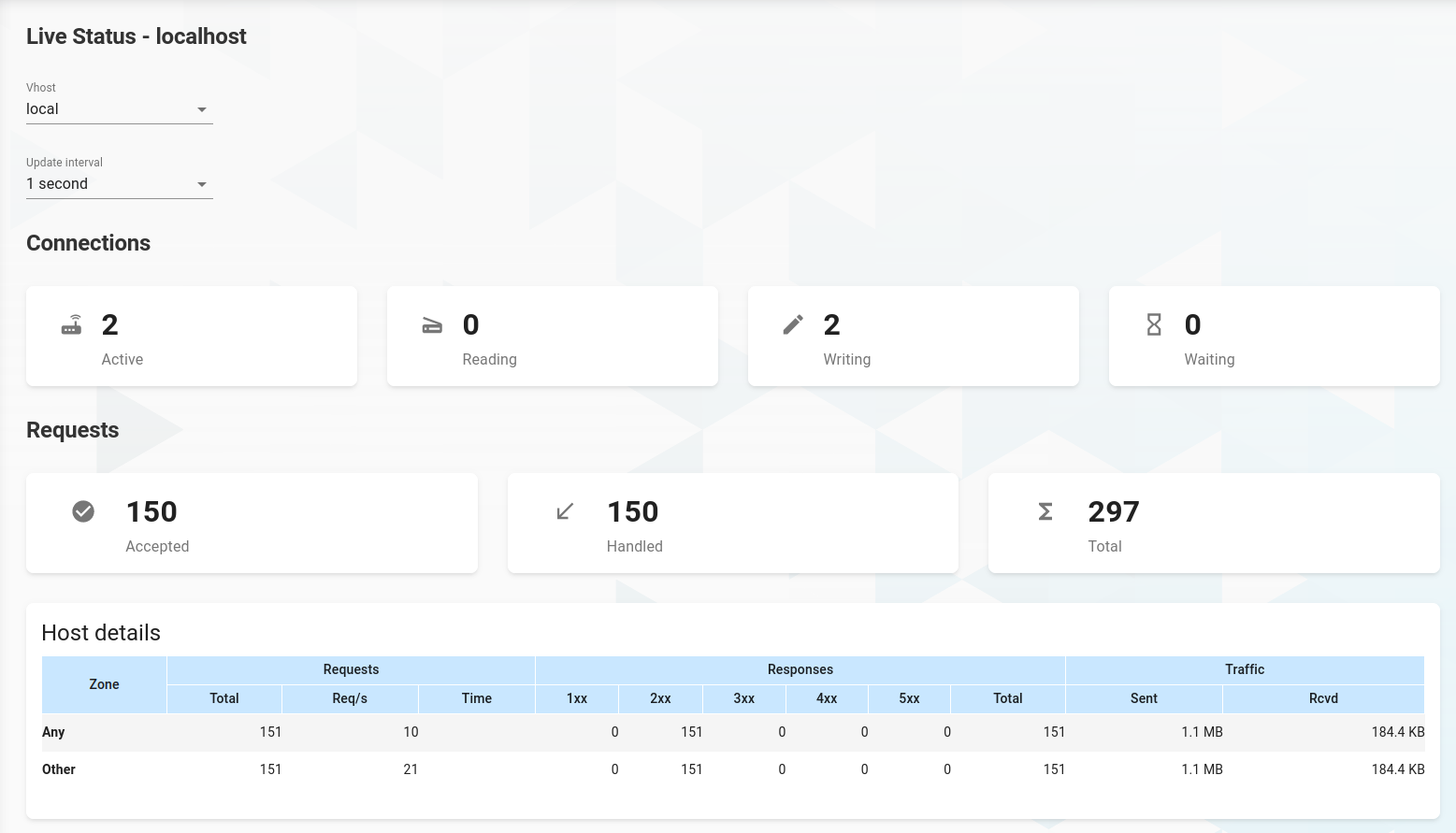
At the top you can select one of the available vhosts and the update interval.
grommunio admin CLI (ACLI)
grommunio-admin
grommunio-admin is the command line interface tool of the grommunio Admin
API. grommunio-admin is a low level administrative tool for grommunio
configuration and provides a large number of subcommands to administrate
grommunio accordingly.
grommunio-admin also provides bash completion functionality and an interactive shell, with the following subcommands available:
config |
Show or check configuration. See `grommunio-admin-config`_. |
connect |
Connect to remote CLI. See `grommunio-admin-connect`_. |
dbconf |
Database-stored configuration management. See grommunio-admin-dbconf. |
domain |
Domain management. See `grommunio-admin-domain`_. |
fetchmail |
Fetchmail management for retrieval of remote mails. See `grommunio-admin-fetchmail`_. |
fs |
Filesystem operations. See `grommunio-admin-fs`_. |
ldap |
LDAP/Active Directory configuration, diagnostics and synchronization. See `grommunio-admin-ldap`_. |
mconf |
Managed configurations manipulation. See `grommunio-admin-mconf`_. |
mlist |
Mailing/distribution list management. See `grommunio-admin-mlist`_. |
passwd |
Internal user password management. See `grommunio-admin-passwd`_. |
run |
Run the REST API. See `grommunio-admin-run`_. |
shell |
Start interactive shell. See `grommunio-admin-shell`_. |
taginfo |
Print information about MAPI property tags. See `grommunio-admin-taginfo`_. |
user |
User management. See `grommunio-admin-user`_. |
version |
Show version information. See `grommunio-admin-version`_. |
SPDX-License-Identifier: CC-BY-SA-4.0 or-later SPDX-FileCopyrightText: 2021 grommunio GmbH
Name
grommunio-admin config — grommunio-admin config introspection
Synopsis
Commands
check
dump, get
sync.defaultPolicy)trace
files), showing which parts of
a file are actually used, or by value (values), showing which file each
value originates from.termcolor package is advised for a more
readable output. See section Tracing for more information.Options
KEYOnly view specified key.
-s,--show-historyDisplay more value history (see section Tracing for more information)
Tracing
By-File
+, green: The value is part of the final configuration
x, red: The value is overwritten by a later file
*, yellow: The object or list is extended by a later file
~, grey: The value is overwritten with the same value
By-Value
SPDX-License-Identifier: CC-BY-SA-4.0 or-later SPDX-FileCopyrightText: 2020-2021 grommunio GmbH
Name
grommunio-admin connect — Connect to remote CLI
Synopsis
grommunio-admin connect [-c COMMAND] [--no-verify] [--redirect-fs [--auto-save (local|remote|discard|print)]] [-v] [HOST [USER [PASSWORD]]]
Description
SystemAdminPermission.Note that the remote CLI currently uses a REST interface which does not provide a standard input, rendering commands that rely on user interaction useless.
Options
HOSTHost to connect to, in the format protocol://hostname:port, where protocol is either http or https. If omitted, the protocol is auto-detected, with https taking precedence over http. If no port is specified, the default ports 8080 (http) and 8443 (https) are used. hostname can either be a resolvable host name, an IPv4 address or an IPv6 address in brackets. The default hostname is localhost.
PASSWORDPassword to use for authentication. Default is to prompt.
USERUser to use for authentication. Default is admin.
--auto-save ACTIONChoose automatic action for received files when filesystem redirection is enabled. Possible actions are:
discard - discard any received filelocal - save at local pathprint - print file contents to stdout and discardremote - save at path reported from remote server-c,--commandExecute command on remote server and exit instead of starting an interactive shell.
--no-verifyContinue with https even if the TLS certificate presented by the server is invalid. Required if the server uses a self-signed certificate that is not installed on the system. Use with caution.
-p,--passwordPrompt for password even when connecting to localhost.
--redirect-fsRedirect CLI initiated file operations to local filesystem. See section Filesystem Emulation for details.
-v,--verbosePrint more detailed information about the connection process.
Filesystem Emulation
When the --redirect-fs option is given, CLI initiated file operations are performed in an emulated filesystem and written files are sent back to the client.
Note that this does only apply to files which are opened by CLI operations, while module-level operations (e.g. loading of configurations) are unaffected.
Files received from the remote server can then be viewed or saved locally.
grommunio-admin-dbconf
Name
grommunio-admin dbconf — Database-stored configuration management.
Synopsis
Description
Configurations consist of key/value pairs organized in files, grouped by service. Each service can have an arbitrary number of configuration files, which in turn can contain an arbitrary number of unique keys.
Commands
commitTrigger commit hook for service, file or key
deleteDelete service, file or key
getGet file or single key
listList available services, files or keys
setSet a configuration key
Options
SERVICEName of the service to configure
FILEName of the configuration file
KEYName of the configuration key
VALUEValue to store in the key
--Indicate that all options have been specified and only names follow
-b,--batchDo not auto-commit
-i,--initOnly set if configuration key does not exist yet
grommunio-admin
The grommunio-admin API and CLI are also dbconf consumers. This allows system adiministrators to change certain configurations without filesystem access and the need to restart the API.
The following files and keys are meaningful when placed under the grommunio-admin service:
multi-server
policyServer selection policy for newly created users and domains in multi-server environments. Possible values are balanced, first, last, random and round-robin. Default is round-robin.
Commit Hooks
When modifying values, potential consumers can be notified of this change via commit hooks, for example by restarting the service using the configuration. For security reasons only a few white-listed commands are available (see section AVAILABLE COMMIT COMMANDS).
Commit hooks can be defined on key, file or service level.
set operations always trigger commits at key level, while the commit
command can directly trigger key or service level hooks depending on
whether a file or key is specified.
If no hook is defined for a specific trigger level, it automatically falls through to the next lower level, in the order key > file > service.
Commit hooks for a service can be defined by setting commit_key,
commit_file and commit_service keys under
grommunio-dbconf/<service> to a valid command (see below).
Available Commit Commands
The following commands are available:
Key
postconf -e $ENTRY
File
postconf -e $FILE_S && systemctl reload postfix
Service
systemctl reload $SERVICEsystemctl restart $SERVICEMacros
As the whitelisted commands might be hard to memorize and may be changed in the future, macros are provided that expand to whitelisted commands.
The following macros are defined:
Key
#POSTCONF -> postconf -e $ENTRY
File
#POSTCONF -> sudo postconf -e $FILE_S && systemctl reload postfix
Service
#RELOAD -> systemctl reload $SERVICE#RESTART -> systemctl restart $SERVICECommand Variable Expansion
Commands can contain $-prefixed variables that are expanded before execution. The literal $$ can be used to generate a single $.
The following variables are valid:
ENTRYExpands to
$KEY=$VALUE(key level only)FILEComplete content of the modified file as newline separated key=value entries (file level only)
FILE_SComplete content of the modified file as space separated key=value entries (file level only)
FILENAMEName of the modified file (key and file level)
KEYThe modified key (key level only)
SERVICEName of the modified service
VALUENew value of the modified key (key level only)
SPDX-License-Identifier: CC-BY-SA-4.0 or-later SPDX-FileCopyrightText: 2021-2022 grommunio GmbH
Name
grommunio-admin domain — Domain management
Synopsis
Description
Subcommand to show and manipulate domains.
Commands
createCreate a new domain
deleteSoft-delete a domain
listList domains
modifyModify domain
purgePermanently delete domain
queryQuery domain attributes
recoverRecover a soft-deleted domain
showShow detailed information about a domain
Options
ATTRIBUTEAttributes to query. Available attributes are ID, activeUsers, address, adminName, chat, chatID, displayname, domainStatus, domainname, endDay, homedir, homeserverID, inactiveUsers, maxUser, orgID, tel and title
If no attributes are specified, ID, domainname and domainStatus are shown.
DOMAINNAMEComplete name of the domain
DOMAINSPECDomain name prefix or domain ID
--create-roleAutomatically create a domain administrator role for the new domain
--filesAlso delete files from disk
-f FIELD=<value>,--filter FIELD=<value>Filter expression in the form of ‘field=value’. Can be specified multiple times to refine filter
--format FORMATOutput format. Can be one of csv, json-flat, json-kv, json-object, json-structured and pretty. Default is pretty.
- `` --homeserver HOMESERVER``
ID of the homeserver to place the domain on
--no-defaultsDo not apply configured default values
--separator SEPARATORString to use for column separation (csv and pretty only). Must have length 1 if format is csv. Default is "," for csv and " " for pretty.
-s FIELD,--sort FIELDSort by field. Can be given multiple times
-y,--yesAssume yes instead of prompting
Fields
--address ADDRESSContent of address field
--adminName ADMINNAMEName of the domain administrator or primary contact
--endDay ENDDAYDate of domain expiration in YYYY-MM-DD format
--orgID IDID of the organization to assign the domain to
--tel TELTelephone number of domain administrator or primary contact
-u MAXUSER,--maxUser MAXUSERMaximum number of users in the domain
SPDX-License-Identifier: CC-BY-SA-4.0 or-later SPDX-FileCopyrightText: 2022 grommunio GmbH
Name
grommunio-admin exmdb — User or domain store management
Synopsis
Description
Subcommand to access and modify a domain's or user's store via exmdb protocol.
Commands
Folder subcommand
createCreate a new folder
deleteDelete folder by ID or name.
findFind folders with given name
grantGrant permissions on this folder to a user
listList subfolders of a folder. If no folder ID is specified, list subfolders of root folder.
revokeRevoke permissions on this folder from a user. If not permission is specified, revoke all permissions.
Store subcommand
deleteDelete properties
getGet store properties
setSet store properties
Options
IDID of the folder
FOLDERSPECID or name of the folder
NAMEName of the folder
PARENTIDID of the parent folder
PERMISSIONName or numeric value of the permission
PROPSPECName or numeric value of the property
TARGETName of the domain or e-mail address of the user
USERNAMEE-Mail address of a user
-a,--allDo not stop if target is ambiguous but apply to all.
--clearDelete folder contents. Required for non-empty folders.
--comment COMMENTFolder comment
-f,--forceGrant permissions to non-existing user
--format FORMATOutput format. Can be one of csv, json-flat, json-kv, json-object, json-structured and pretty. Default is pretty.
-r,--recursiveApply recursively to subfolders
--separator SEPARATORString to use for column separation (csv and pretty only). Must have length 1 if format is csv. Default is "," for csv and " " for pretty.
-t TYPE,--type TYPECONTAINERCLASS property, defaults to "IPF.Note"
-x,--exactOnly match exact folder names instead of case-insensitive substrings
Notes
Folder IDs and permissions can be given in decimal, hexadecimal (0x-prefix), octal (0-prefix) or binary (0b-prefix).
Currently, the permission value echoed by the grant and revoke commands is the one sent to the server and might differ from the value actually assigned.
The create, find and list commands operate on the IPMSUBTREE folders (0x9 for users, 0x2 for domains) by default, which can be overridden by the ID parameter.
SPDX-License-Identifier: CC-BY-SA-4.0 or-later SPDX-FileCopyrightText: 2021-2022 grommunio GmbH
Name
grommunio-admin fetchmail — Manage fetchmail settings and generate rc file
Synopsis
Description
Subcommand to show and manipulate fetchmail entries and generate fetchmailrc file.
Commands
createCreate a new fetchmail entry
deleteDelete fetchmail entry
listList fetchmail entries
modifyModify fetchmail entry
printPrint fetchmail configuration line generated by the entry
showShow detailed information about fetchmail entry
write-rcWrite fetchmail configuration file (fetchmailrc)
Options
MAILBOXE-Mail address of the local mailbox to deliver the mails to. Defaults to e-mail address of the specified user
MBSPECMailbox prefix or ID of the fetchmail entry
USERSPECUsername prefix or ID of the user to attach the entry to
-f FIELD=<value>,--filter FIELD=<value>Filter expression in the form of ‘field=value’. Can be specified multiple times to refine filter
--forceWrite rc file even if no entries were changed since the last write
-o,--out-filePath to write configuration to. Default is /etc/fetchmailrc
--passwordPrint the source password
-p,--printAdditionally print rc file to stdout
-q,--quietDo not print additional info
-s FIELD,--sort FIELDSort by field. Can be given multiple times
-t,--timeTime in minutes since the last write. Default is to autodetect by file mtime
-v,--verboseBe more verbose
-y,--yesDelete multiple entries without prompting
Fields
--active STATEWhether the entry is active. STATE can be one of 0, 1, yes or no. Default is 1
--extraOptions EXTRAOPTIONSSpace separated list of options to write into the fetchmailrc
--fetchall STATEWhether to fetch mails marked as seen on the source server. STATE can be one of 0, 1, yes or no. Default is 0
--keep STATEWhether to keep fetched mails on the source server. STATE can be one of 0, 1, yes or no. Default is 1
--protocol PROTOCOLProtocol to use for fetching. Can be one of POP3, IMAP, POP2, ETRN or AUTO. Default is IMAP
--srcAuth AUTHAuthentication method to use. Can be one of password, kerberos_v5, kerberos, kerberos_v4, gssapi, cram-md5, otp, ntlm, msn, ssh, any. Default is password
--srcFolder FOLDERSource folder to fetch from
--srcPassword PASSWORDPassword of the source user. Single (') and double (") quotes are automatically removed.
--srcServer SERVERSource server to fetch from
--srcUser USERSource user to fetch mails from
--sslCertCheck STATEWhether to force SSL certificate check. STATE can be one of 0, 1, yes or no. Default is 0
--sslCertPath SSLCERTPATHPath to a directory containing trusted certificates or empty to use system default
--useSSL STATEEnable SSL
SPDX-License-Identifier: CC-BY-SA-4.0 or-later SPDX-FileCopyrightText: 2021-2022 grommunio GmbH
Name
grommunio-admin fs — Filesystem operations
Synopsis
Description
Show space used by user and domain home directories or remove unused files.
Unused files may remain when users or domains are deleted without removing their files.
Commands
cleanRemove directories and files that are not used by any domain or user.
duShow data usage statistics
Options
PARTITIONApply only to selected partition. Can be either domain or user
-d,--dryrunDo not delete anything, just print what would be deleted
-s,--nostatDo not collect disk usage statistics of deleted files
SPDX-License-Identifier: CC-BY-SA-4.0 or-later SPDX-FileCopyrightText: 2021-2022 grommunio GmbH
Name
grommunio-admin ldap — LDAP tools
Synopsis
Description
The grommunio admin ldap module provides functions for configuring and testing the LDAP connection and downloading or updating users.
Commands
checkCheck if the LDAP objects imported users are linked to can still be found, optionally removing orphaned users
configureInteractively configure or modify LDAP connection
downsyncSynchronize or import users from LDAP
dumpPrint LDAP object
infoShow connection status
reloadReload the LDAP configuration and reconnect
searchSearch for users
Options
USERLDAP object ID or search string
-a,--allShow all results, not only importable objects
--auth-backend <automatic|externid|always_ldap|always_mysql>For reload only. Set the authmgr global system authentication backend. Can be one of automatic (same as externid), externid, always_ldap, always_mysql. Default is externid if unset.
-c,--completeImport or update all users from the LDAP tree
-f,--forceForce update users that are linked to a different or no LDAP object
--format FORMATOutput format. Can be one of csv, json-flat, json-kv, json-object, json-structured and pretty. Default is pretty.
-l,--langSet language for imported users. Default is to not set any language.
-m,--remove-maildirsAlso remove user files from disk
-n MAX_RESULTS,--max-results MAX_RESULTSMaximum number of results or 0 to disable limit (default 0). Note that the actual number of results may exceed the limit due to paging and filtering.
-o ORGSPEC,--organization ORGSPECUse organization specific LDAP connection. Supports organization ID or name.
-p PAGE_SIZE,--page-size PAGE_SIZESet batch size for paged search. Can be decreased when running into timeout errors with slow LDAP servers. Default is 1000.
-r,--removeRemove imported users of which the linked LDAP object could not be found
-t TYPES,--types TYPESComma separated list of object types to search for. Supported are user, contact and group.
-x <bool>,--disable-ldap <bool>For reload only. Set the disable LDAP switch for the organization or globally system wide.
-y,--yesDo not prompt for confirmation, assume yes
SPDX-License-Identifier: CC-BY-SA-4.0 or-later SPDX-FileCopyrightText: 2021 grommunio GmbH
Name
grommunio-admin mconf — Managed configuration manipulation
Synopsis
Description
grommunio managed configuration (mconf) offers the possibility to manipulate configuration files used by gromox.
Commands
dumpPrint configuration file that would be generated from internal state
modifyModify internal configuration state
printPrint internal configuration state
reloadReload configuration from disk
saveSave configuration file to disk
Options
ACTIONModification action:
add - Add entry to listremove - Remove entry from listset - Add keyunset - Remove keyCONFIGConfiguration file, either authmgr or ldap
KEYConfiguration key
VALUEConfiguration value for numeric or boolean values use -b and -i respectively
-b,--boolConvert value to boolean, valid values are y, n, yes, no, true, false, 1, 0
-c,--censorHide confidential information
-i,--intConvert value to integer, octal (0o) and hexadecimal (0x) prefixes are supported
SPDX-License-Identifier: CC-BY-SA-4.0 or-later SPDX-FileCopyrightText: 2021 grommunio GmbH
Name
grommunio-admin mlist — Mailing/distribution list management
Synopsis
Description
Create, modify or delete mailing lists.
Commands
addAdd sender or recipient to list
createCreate a new mailing list
deleteDelete mailing list
listList mailing lists
modifyModify mailing list
removeRemove sender or recipient from list
showShow detailed information about mailing list
Options
-p PRIVILEGE,--privilege PRIVILEGESet who is allowed to send mails to the list, one of all, domain, internal, outgoing or specific
-f FIELD=<value>,--filter FIELD=<value>Filter expression in the form of ‘field=value’. Can be specified multiple times to refine filter
-s FIELD,--sort FIELDSort by field. Can be given multiple times
-t TYPE,--type TYPEList type (recipient selection), one of normal or domain
SPDX-License-Identifier: CC-BY-SA-4.0 or-later SPDX-FileCopyrightText: 2024 grommunio GmbH
Name
grommunio-admin org — Organization management
Synopsis
Description
Subcommand to show and manipulate organizations.
Commands
createCreate a new organization
deleteDelete an organization
modifyModify organization
queryQuery organization attributes
showShow detailed information about an organization
Options
ATTRIBUTEAttributes to query. Available attributes are ID, name, description and domainCount
If no attributes are specified, ID, name and domainCount are shown.
ORGNAMEComplete name of the organization
ORGSPECOrganization name prefix or organization ID
-f FIELD=<value>,--filter FIELD=<value>Filter expression in the form of ‘field=value’. Can be specified multiple times to refine filter
--format FORMATOutput format. Can be one of csv, json-flat, json-kv, json-object, json-structured and pretty. Default is pretty.
--separator SEPARATORString to use for column separation (csv and pretty only). Must have length 1 if format is csv. Default is "," for csv and " " for pretty.
-s FIELD,--sort FIELDSort by field. Can be given multiple times
-y,--yesAssume yes instead of prompting
Fields
--description DESCRIPTIONDescription of the organization
--domain DOMAINSPECName prefix or ID of the domain to adopt. Can be given multiple times
--name ORGNAMEName of the organization
SPDX-License-Identifier: CC-BY-SA-4.0 or-later SPDX-FileCopyrightText: 2021 grommunio GmbH
Name
grommunio-admin passwd — Set user password
Synopsis
grommunio-admin passwd [-a] [-l LENGTH] [-p PASSWORD] [USER]
Description
Options
USERUser to set password for (default admin)
-a,--autoAutomatically generate a password
-l LENGTH,--length LENGTHLength of the automatically generated password (default 16)
-p PASSWORD,--password PASSWORDPassword to set (do not prompt)
SPDX-License-Identifier: CC-BY-SA-4.0 or-later SPDX-FileCopyrightText: 2021-2022 grommunio GmbH
Name
grommunio-admin run — Start a stand-alone HTTP server
Synopsis
grommunio-admin run [-d] [-i IP] [--no-config-check] [-p PORT]
Description
Run REST API in a stand-alone HTTP server.
Options
-d,--debugEnable debug mode
-i IP,--ip IPHost address to bind to (default ::)
--no-config-checkSkip configuration check
-p PORT,--port PORTHost port to bind to (default 5001)
SPDX-License-Identifier: CC-BY-SA-4.0 or-later SPDX-FileCopyrightText: 2022 grommunio GmbH
Name
grommunio-admin server — Multi-server management
Synopsis
Description
Subcommand to show and manipulate server entries.
If at least one server is specified, newly created users and domains will be associated with one of the servers. The destination server may be specified explicitly, or is chosen automatically according to options.serverPolicy.
Commands
createRegister a new server
deleteSoft-delete a server
listList domains
modifyModify server
showShow detailed information about a server
Options
SERVERSPECServer hostname or ID
-f FIELD=<value>,--filter FIELD=<value>Filter expression in the form of ‘field=value’. Can be specified multiple times to refine filter
-s FIELD,--sort FIELDSort by field. Can be given multiple times
Fields
-H HOSTNAME,--hostname HOSTNAMEInternal hostname of the server
`-e EXTNAME,--extname EXTNAMEExternal hostname (e.g. FQDN) of the server.
SPDX-License-Identifier: CC-BY-SA-4.0 or-later SPDX-FileCopyrightText: 2021-2022 grommunio GmbH
Name
grommunio-admin service — grommunio-admin external service interface control
Synopsis
Description
UNLOADEDThe service has not been loaded yet. It will be loaded automatically when needed.
LOADEDThe service has been initialized successfully.
UNAVAILABLEAn error occurred that indicates that the service is not available, but might become available in the future. No reload is necessary to reconnect.
SUSPENDEDÀn error occurred that indicates that the service is not available, but might become available in the future. The service will be reloaded automatically on next usage.
ERRORThe service is not available either because initialization failed or because to man errors occurred. It will remain unavailable until reloaded manually.
DISABLEDThe service has been manually disabled (either by configuration or command).
Commands
load
status
Options
SERVICEName of the service.
-r,--reloadForce reload of service.
-v,--verboseShow more information.
Services
The following services are currently connected via the service interface:
chatgrommunio chat. Connected via REST interface.
exmdbgromox exmdb provider (gromox-http). Connected via custom TCP protocol.
ldapExternal LDAP service. Connected via LDAP(s).
redisRedis instance (used by grommunio sync). Connected via redis driver (TCP).
systemdSystemd shell execution.
SPDX-License-Identifier: CC-BY-SA-4.0 or-later SPDX-FileCopyrightText: 2021 grommunio GmbH
Name
grommunio-admin shell — Start interactive shell
Synopsis
grommunio-admin shell [-d] [-n] [-x]
Description
The interactive shell mode allows execution of multiple (new line separated) commands in a single session. Command syntax is identical to the CLI arguments, with addition of the exit command which ends the interactive shell.
If possible, typed history will be saved in ~/.grommunio-admin.history.
Options
-d,--debugEnable more verbose debug output
-n,--no-historyDisable loading/saving of the typed history
-x,--exitExit immediately if a command results in a non-zero exit code
SPDX-License-Identifier: CC-BY-SA-4.0 or-later SPDX-FileCopyrightText: 2021-2022 grommunio GmbH
Name
grommunio-admin taginfo — Show information about proptags
Synopsis
grommunio-admin taginfo TAG [TAG …]
Description
Options
TAGDecimal or hexadecimal (with 0x prefix) Tag ID or grommunio tag name glob
SPDX-License-Identifier: CC-BY-SA-4.0 or-later SPDX-FileCopyrightText: 2021-2022 grommunio GmbH
Name
grommunio-admin user — User management
Synopsis
Description
Subcommand for user management.
Commands
createCreate a new user
delegateManage delegate permission
deleteDelete user
devicesUser mobile device management
listList users Deprecated. Use query instead.
loginTest user login
modifyModify a user
queryQuery user attributes
sendasManage send-as permission
showShow detailed information about a user
Options
ATTRIBUTEAttributes to query. Available attributes are ID, aliases, changePassword, chat, chatAdmin, domainID, forward, homeserverID, lang, ldapID, maildir, pop3_imap, privArchive, privChat, privFiles, privVideo, privWeb, privDav, privEas, publicAddress, smtp, status and username.
If no attributes are specified, ID, username and status are shown.
DEVICELimit command to given device ID(s)
USERNAMEE-Mail address of the user
USERSPECUser name prefix or user ID
-c,--keep-chatDeactivate but do not permanently delete chat user
--delete-chat-userPermanently delete chat user
-f FIELD=<value>,--filter FIELD=<value>Filter expression in the form of ‘field=value’. Can be specified multiple times to refine filter
--format FORMATOutput format. Can be one of csv, json-flat, json-kv, json-object, json-structured and pretty. Default is pretty.
-k,--keep-filesDo not delete user files from disk
--mode MODESpecify wipe status to set. Possible values are account and normal, or cancel to stop a pending wipe.
--no-defaultsDo not apply configured default values
--no-ldapDetach user from LDAP object
--no-maildirDo not create a mailbox for that user
--nopassSkip password check
--passwordUser password. If omitted, password is retrieved from prompt.
--remove-alias ALIASRemove ALIAS from user (can be given multiple times)
--remove-altname ALTNAMERemove ALTNAME from user (can be given multiple times)
--remove-property PROPSPECRemove property from user (can be given multiple times)
--remove-storeprop PROPSPECRemove property from user's store (can be given multiple times)
--separator SEPARATORString to use for column separation (csv and pretty only). Must have length 1 if format is csv. Default is "," for csv and " " for pretty.
-s FIELD,--sort FIELDSort by field. Can be given multiple times
--tokenGenerate access and CSRF token on successful login
-y,--yesAssume yes instead of prompting
Fields
--changePassword <bool>Whether the user can change the password
--chat <bool>Whether to create a chat user
--chatAdmin <bool>Whether the user has chat admin privileges
--homeserver IDID of the home server or 0 for local user
--lang LANGUser store language
--ldapID LDAPIDIdentifier of the LDAP object linked to the user
--pop3-imap <bool>Whether the user has the POP3/IMAP privilege
--privArchive <bool>Whether the user has the archiving privilege
--privChat <bool>Whether the user has the chat privilege
--privFiles <bool>Whether the user has the files privilege
--privVideo <bool>Whether the user has the video privilege
--privWeb <bool>Whether the user has the web privilege
--privDav <bool>Whether the user has the DAV privilege
--privEas <bool>Whether the user has the EAS privilege
--public-address <bool>Whether the user has the public address privilege
--smtp <bool>Whether the user has the SMTP privilege
--status STATUSUser address status. Either numeric value or one of normal, suspended, deleted or shared.
--alias ALIASAdd alias
--altname ALTNAMEAdd ALTNAME to user alternative login name list (can be given multiple times)
--property propspec=valueSet property defined by propspec to value
--storeprop propspec=valueSet store property defined by propspec to value
--usernameRename user
SPDX-License-Identifier: CC-BY-SA-4.0 or-later SPDX-FileCopyrightText: 2021 grommunio GmbH
Name
grommunio-admin version — Show backend and/or API version
Synopsis
grommunio-admin version [-a] [-b] [-c]
Description
If multiple options are given, each requested version is printed on a separate line. The order is always API – backend – combined.
Options
-a,--apiPrint API version
-b,--backendPrint backend version
-c,--combinedPrint combined version