Outlook bugs and issues
Attachment size
Situation: When looking a mail that has attachments, the size reported next to the icon+filename appears inflated over the actual file size that will be saved to disk.
Cause: Outlook displays the value of the PR_ATTACH_SIZE MAPI property. This
property is specified to not only include the file size, but also the metadata
for the attachment.
Restoring softdeleted public folders
When a softdeleted public (sub-)folder is restored, the name is truncated to one character, even with EXC2019 server.
AutoDiscover diagnostics
When Outlook is running, there is an Outlook icon in the Windows taskbar's notification area. By pressing Ctrl+RightMouseBtn, a service menu can be brought up, which offers a "Test AutoDiscover" command for diagnosing problems from Windows. Known bugs: The dialog may ignore the contents of the password field and instead use a saved password or SSO, leading to potentially unanticipated HTTP 401 (Unauthorized) responses. If in doubt, use gromox-dscli.
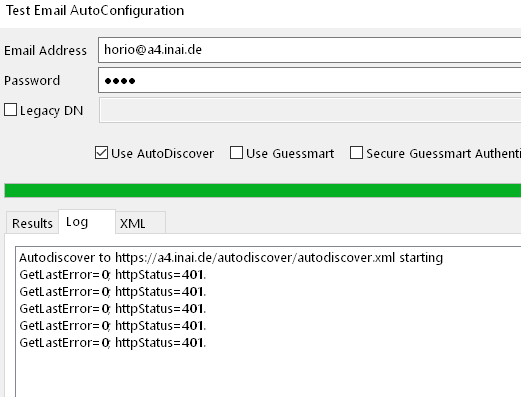
SRV redirection warning
Situation: Outlook shows a redirection warning when the SRV record has a hostname different from the domain.
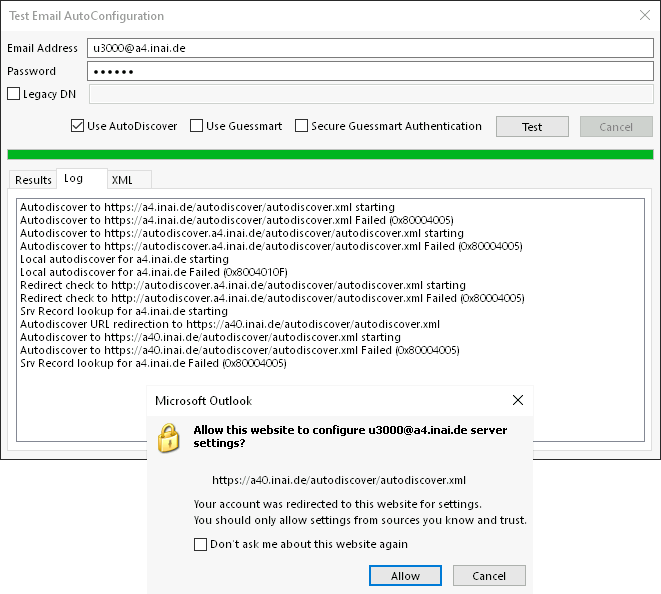
Text: “Allow this website to configure user@example.com server settings? https://mail.example.com/autodiscover/autodiscover.xml . Your account was redirected to this website for settings. You should only allow settings from sources you know and trust. [ ] Don't ask me about this website again.”
Cause: Questionable programming in Outlook and/or Windows's networking libraries. A SRV record has the same security considerations as a CNAME record. (Outlook also ignores the port number in the SRV record.)
Fixes/Workarounds: Report issues to Microsoft. Or use the always-accept
checkbox. Deleting the DNS SRV record is a viable option too, because one can
make a CNAME/A/AAAA-type autodiscover.example.com entry in the DNS zone
instead.
Passwords with umlauts
Gromox conveys the available authentication mechanisms to clients via the
WWW-Authentication header in HTTP responses. As of Gromox 2.17, "Basic" and
"Negotiate" are supported. "Basic" is augmented by a charset parameter (RFC
7617 §2.1).
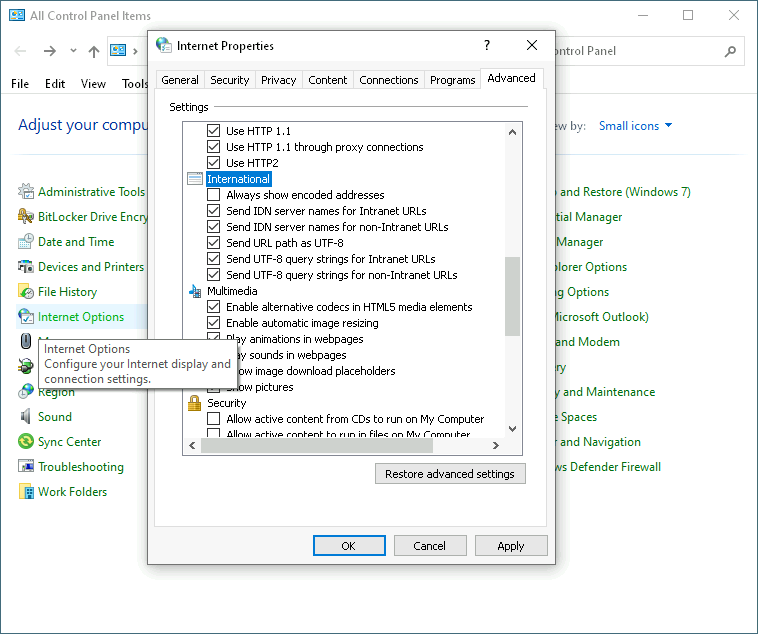
However, the Windows RPC and HTTP libraries ignore this parameter, and they also ignore the few UTF-8 options from the Control Panel's Internet Options dialog.
The RPC/HTTP libraries always transmit Basic authorization using the system
default locale's codepage. In fact, if the password entered into the
authorization dialog cannot be represented in that encoding, no
Authorization header will be sent at all in the HTTP request.
Exchange Server interprets passwords received via the Basic authorization
header as UTF-8 at first and, should the password validation fail, it will
retry using the codepage of the default locale of the server system. This
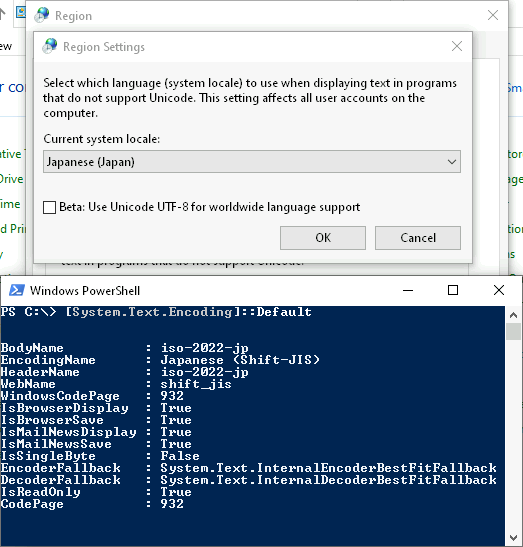
means that a Windows client using Japanese locale (codepage 932) will never be
able to connect to an Exchange Server running with English locale (Codepage
1252) using Basic-type authentication.
Unlike Windows, installations of contemporary Linux systems exclusively use UTF-8. As such, there is no second charset that would make sense for a server process to try.
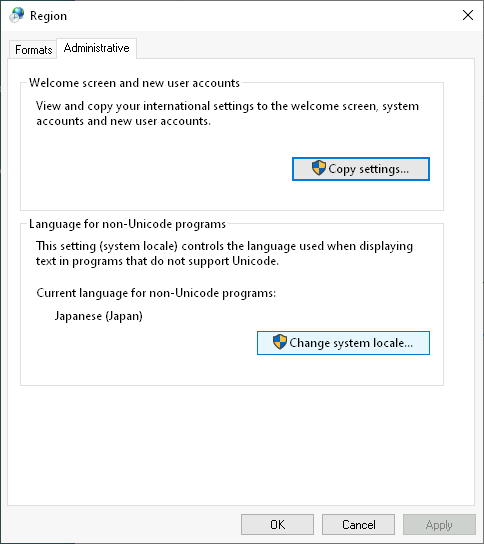
In Windows 10 and later, the Region settings in the (classic) Control Panel has a checkbox to switch the Narrow Encoding System APIs to interpret and emit strings and some other data as UTF-8, much like what Linux systems do. Be aware that changing the region has consequences for all unannotated data. For example, it influences how text editors will make guesses about the encoding of plain-text files.
Authentication via the Negotiate mechanism is believed to be mostly free
from character set problems. Negotiate can contain GSS/SSO/NTLM tokens, and
NTLM in particular is specified to use UCS-2LE/UTF-16LE for its
challenge–response authentication, which gives non-ASCII characters an angle to
survive.
Rules dialog not openable
RuleOrganizer is a FAI message in Inbox with PR_MESSAGE_CLASS="IPM.RuleOrganizer". If this message has no PR_RW_RULES_STREAM property, Outlook refuses to open the rules dialog. It issues a ropOpenStream call without MAPI_CREATE, which means it did not pass MAPI_CREATE to the IMessage::OpenProperty COM API either. Therefore, if the property is missing, OL will will not re-create it (which is stupid, because when the message is absent, it will re-create that).
Moreover, when the PR_RW_RULES_STREAM property exists but has size 0, the rules dialog immediately closes again, another bug.
Offending mailboxes can be repaired with the gromox-mbop -u abc@example.com
clear-rwz command.
MFCMAPI table sort quirk
Sorting a table by clicking on a column header will make MFCMAPI use its own sorting rather than ropSortTable. Only the portion of rows that has already been loaded (ropQueryRows) will be sorted.
Outlook 2010/2013 specialties
Preface summary
At the end of May 2024, this document's German screenshots were slated for replacement with the English version. In that attempt, more weirdness protruded.
English OL2013 15.0.5125.1000 / MAPI 15.0.5449:
If AutoDiscover handler is offering MH: AutoDiscover completes, MAPI profile runs on MH, no traces of RPCH configuration found. All good.
ADH offering only RPCH: The wizard fails the Autodiscover stage. Eventually leads you over to manual setup mode.
Manual setup: The wizard is somehow completely unable to make a successful RPCH connection.
German OL2013 (exact version tbd):
AutoDiscover succeeds, you can also do manual setup, or switch to manual after AD has signalled success. Either way you go, the wizard somehow gets the idea it wants to talk to a magic hostname "SERVERS". You can end the wizard successfully and it believes it has a connection, but actually does not. The MAPI profile remains broken and the bogus RPC server name needs to be edited with MFCMAPI. Once that is done, it actually works very well over RPCH.
Control Panel
Open Control Panel and the E-Mail control widget and create a new profile. Alternatively, new profiles can be created when launching Outlook if and when it shows its profile selection dialog (requires that no profile be marked as default yet).
Special dialog for domain-joined accounts
When creating a new profile in Outlook, you may be presented with a dialog that has only two fields (name, email address), with the name field being filled in and grayed out already. This can happen if the computer is joined to an existing NT/ActiveDirectory domain.
If you were to leave those fields as-is, the wizard might skip AutoDiscover or use the AutoDiscover of the domain controller (especially when there is already an Exchange server). We have observed that, in such a domain, the wizard proceeds and uses the domain controller's name as the RPC server name, thereby causing requests to never reach the Gromox server.
Modifying the email address field value switches the dialog to present the usual four fields. This action would appear to drop the implied default to use the domain controller, which is a good thing.
AutoDiscover
When using automatic mode (i.e. the radiobox "E-mail Account") from the 4(!)-field dialog, the profile wizard proceeds to invoke AutoDiscover. Provided the DNS domain name resolves to a Gromox server, AutoDiscover should succeed, even if joined to an NT domain of the same name.
At this point, you may get a warning if you used a self-signed or otherwise not verifiable TLS certificate. If indeed your Gromox server uses such a certificate, that is a good sign that AutoDiscover did indeed reach the Gromox server.
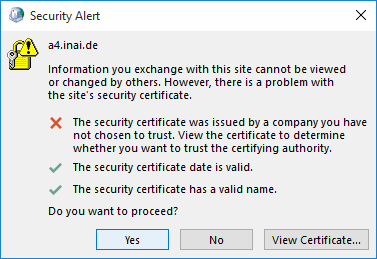
Furthermore, there may be also be a second warning. The AutoDiscovery process
uses a number of techniques, and one of them involves testing for a DNS entry
wherein autodiscover. is prepended to the e-mail domain you entered. If
that DNS entry indeed exists, but is not part of the TLS certificate, the
wizard complains about a certifiace name mismatch.
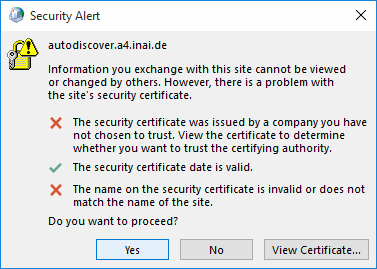
With TLS squared away either with a proper certificate or ignoring the issue, AutoDiscover ought to succeed.
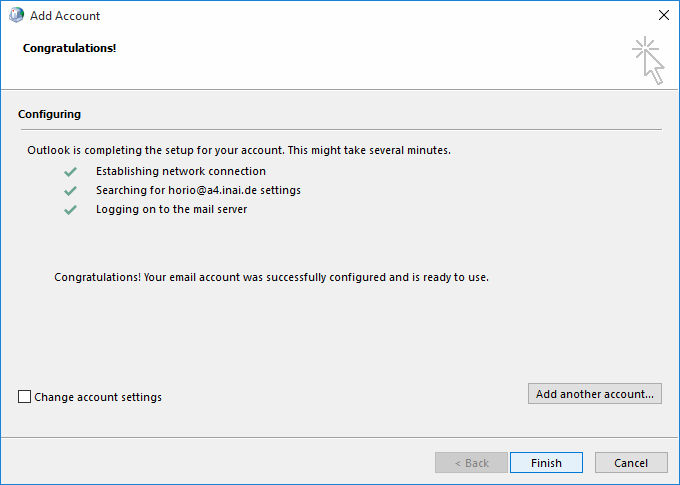
If you get a failure indication instead that an encrypted connection was not possible, that is usually an indication of a DNS or network issue, and attempting an unencrypted AutoDiscover request won't fix that.
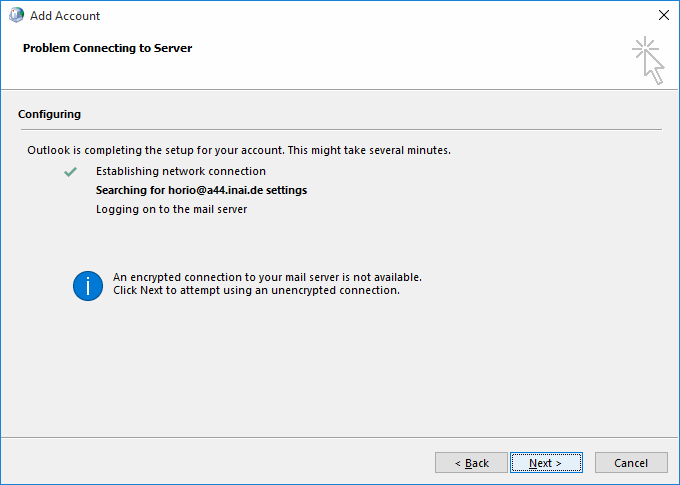
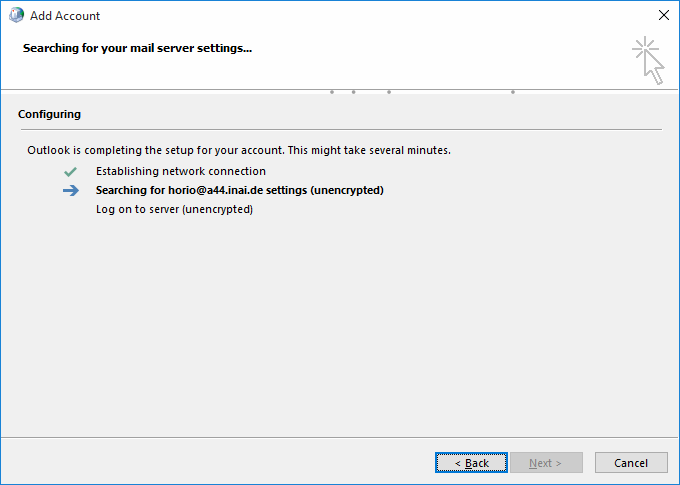
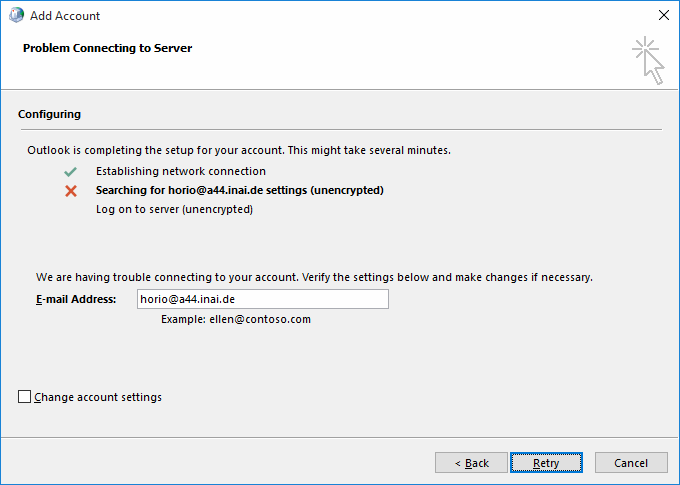
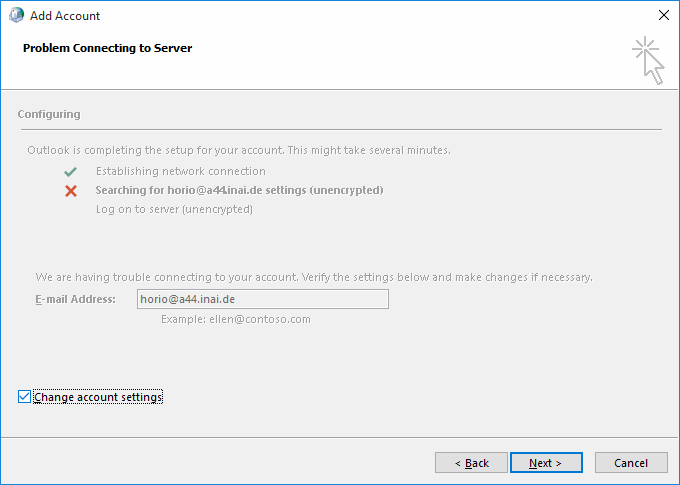
Turning the attention back to the successful AutoDiscover dialog form (with the three green checkmarks), you have the option to switch to manual setup mode using the "Change account settings" checkbox in the lower left of the dialog. Doing so will make the wizard switch to the next dialog state, titled "Server settings".
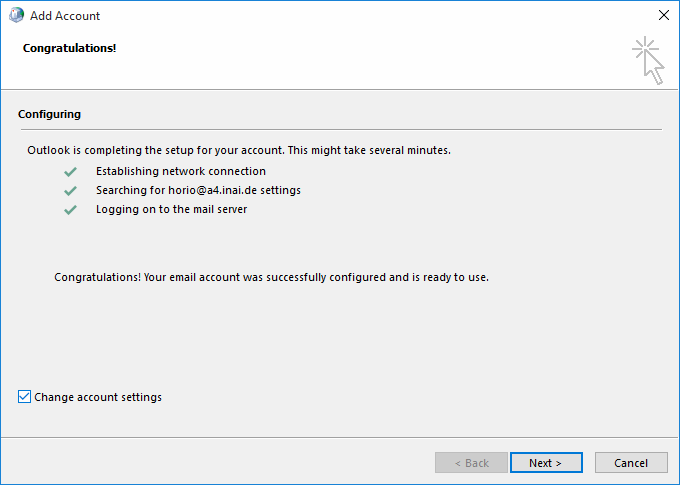
Since this is a technical documentation exploring the quirks of Outlook, we recommend you do this for understanding the following descriptions. Continue reading below at section "RPC hostname troubles".
Manual Setup
If you choose the radiobox "Manual Setup", AutoDiscover will be skipped.
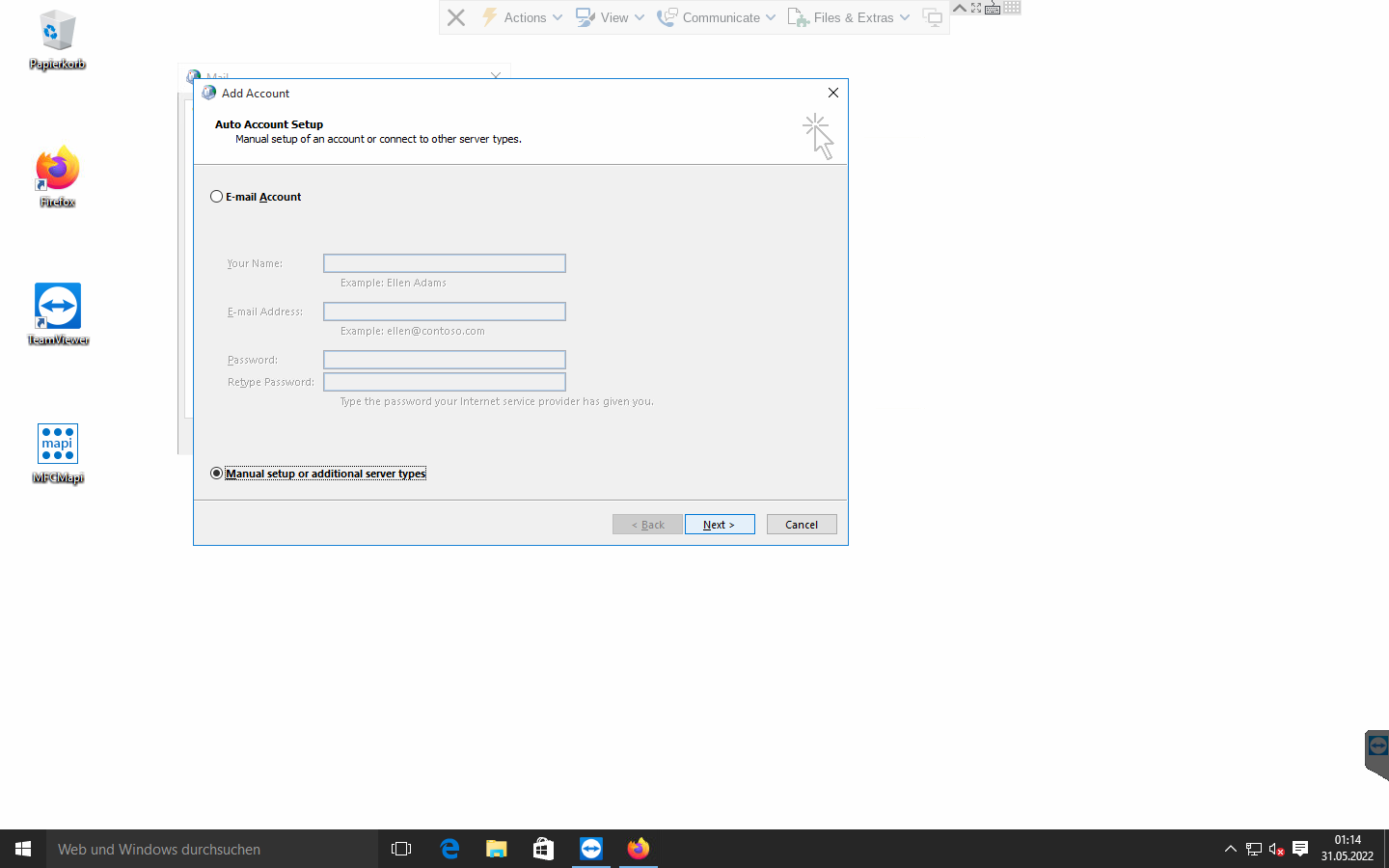
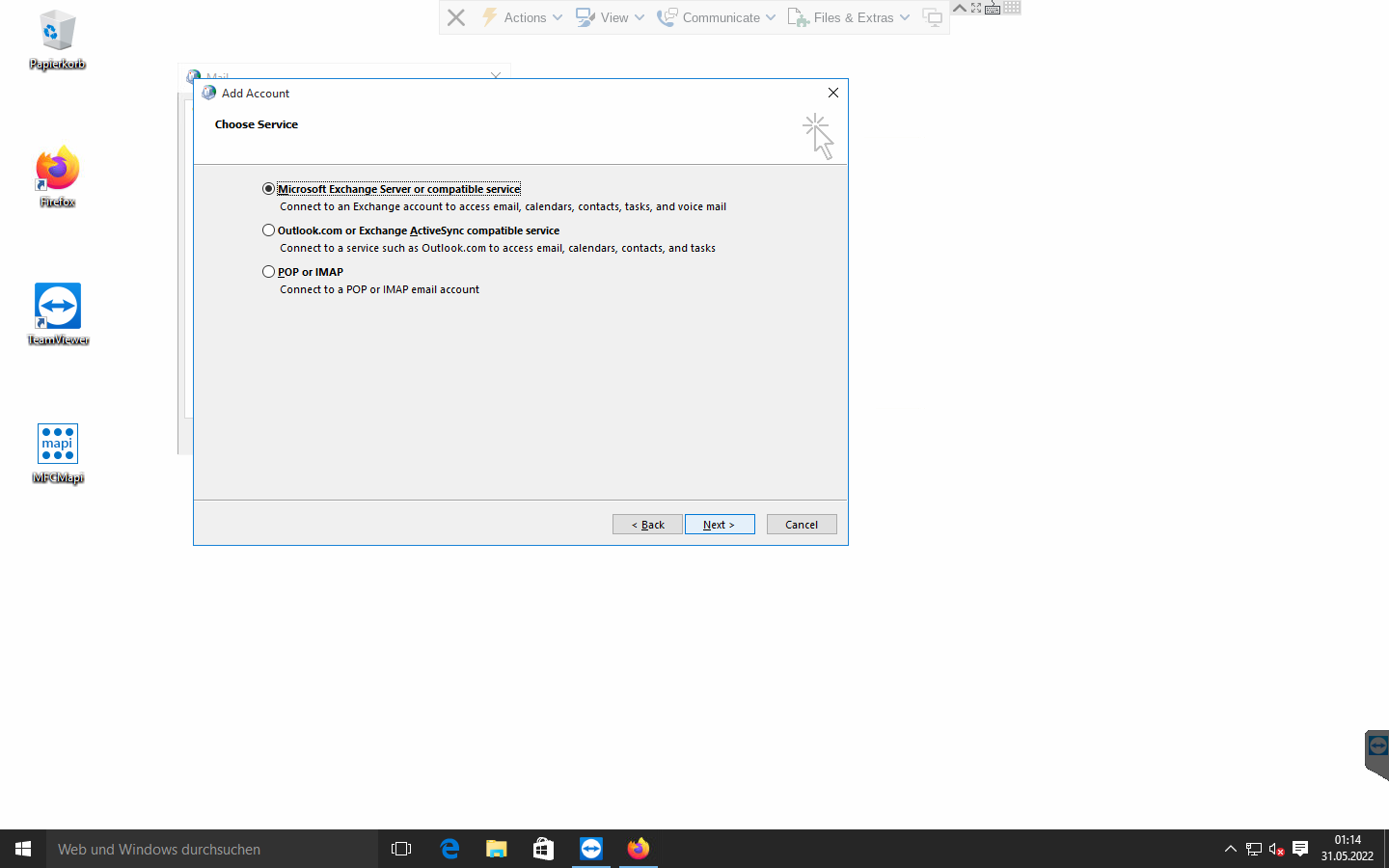
After choosing the Exchange server type radio box, you will proceed to the "Server Settings" view. You should input the server and user name. The OL2013 profile wizard defaults to using RPC over port 135, which is not supported by Gromox, and so using "Check Name" will not function just yet.
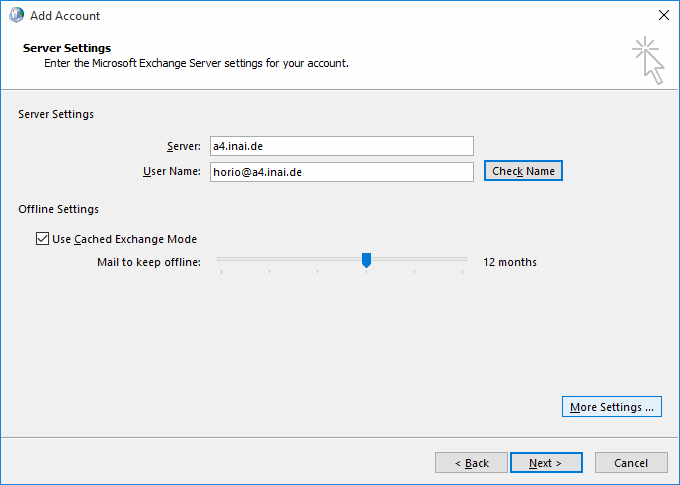
Instead, go to "More Settings" and its Security notebook page, and select "Anonymous Authentication" from the dropdown.
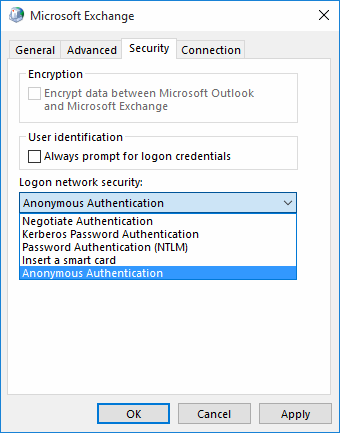
Next, goto More Setting's "Connection" notebook page, enable "Connect using HTTP", and call up the "Proxy Settings" subdialog.
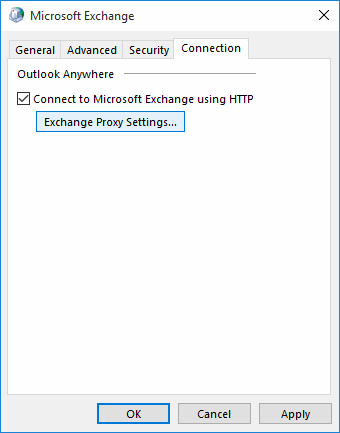
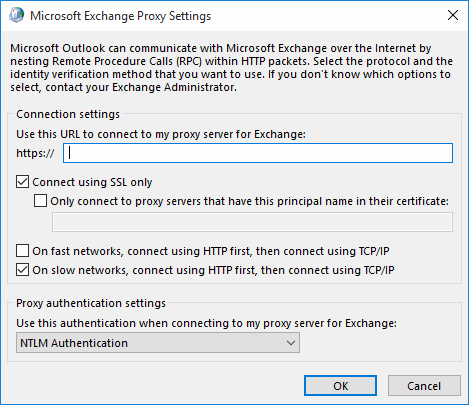
Enter the server name again in the HTTP field, and switch from "NTLM Authentication" to "Basic Authentication".
You should enable both "On fast networks, connect using HTTP first" and "On slow networks, connect using HTTP first".
"Connect using HTTP first, then use TCP/IP" is a misnomer; what it really means "Connecting using RPCHTTP or MAPIHTTP first, then try RPC-over-TCP".
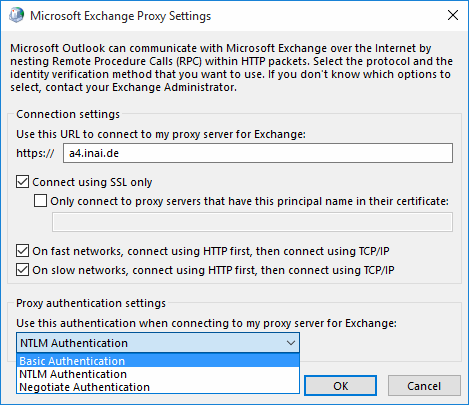
You can close the More Settings subdialog(s).
If you now use the "Check Name" feature, the server and user name field values
should “resolve”, i.e. become underlined. The server name will also change to
an uncanny value of SERVERS.
RPC hostname troubles
If AutoDiscover found the MH/RPCH transport just fine, the "Server Settings" dialog will show someguid@domain in the Server field and the email address in the username field. In addition, under "More Settings", there will only be three tabs and no way to call up the RPC proxy settings.
Now for the odd case with at least one OL2013 variant (German):
Whether you have done Manual Setup or reached this point through AutoDiscover,
you will notice that the RPC server has been changed to the value SERVERS.
We have no indication where this name comes from — searching prominent Windows
DLLs, including, but not limited to, rpcrt4.dll, turns up no string of the
sort, and it is incredibly hard to do an Internet search for the word because a
common word was reused.
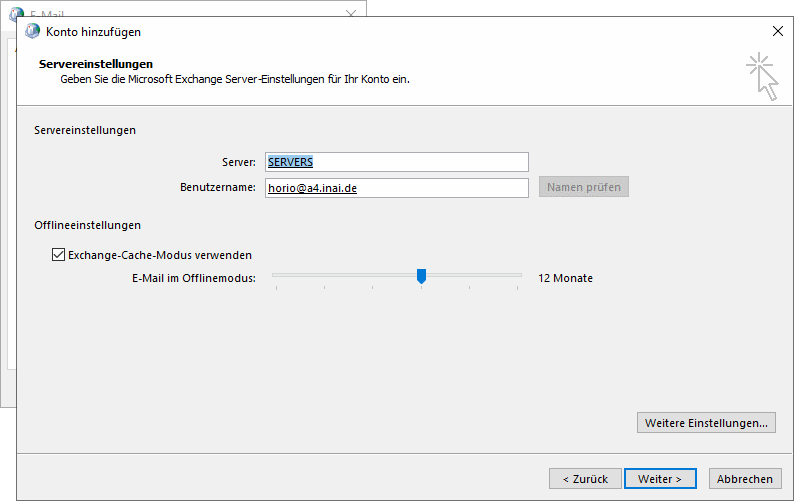
The server and email address are underlined and the "Check Names" button is grayed out, which normally indicates that the two field values have (supposedly) been successfully resolved.
You may finish the profile wizard at this point. Read on for more technical gore though…
Some Windows installations are fine with SERVERS. Some are not. We do not
know exactly why, but one hypothesis is that some versions try to resolve the
RPC server name ahead of the RPCHTTP proxy name. We did observe, with
Wireshark, that name lookups were being done for SERVERS (NBNS, LLMNR
and/or MDNS packets) are being emitted into the network.
By modifying the server or user name field again (e.g. remove last character
and add the character back again), the field values go back to unresolved mode
and the "Check Names" button becomes available again. When that check feature
is used again, the server now magically resolves to a new value in the form of
xxxxxxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xx-xxxxxxxxxxxx@hostname. While we know that this is a
endpoint ID for an RPC proxy and we know where it originates from in the source
code, it also does not help to get the mailbox connection going.
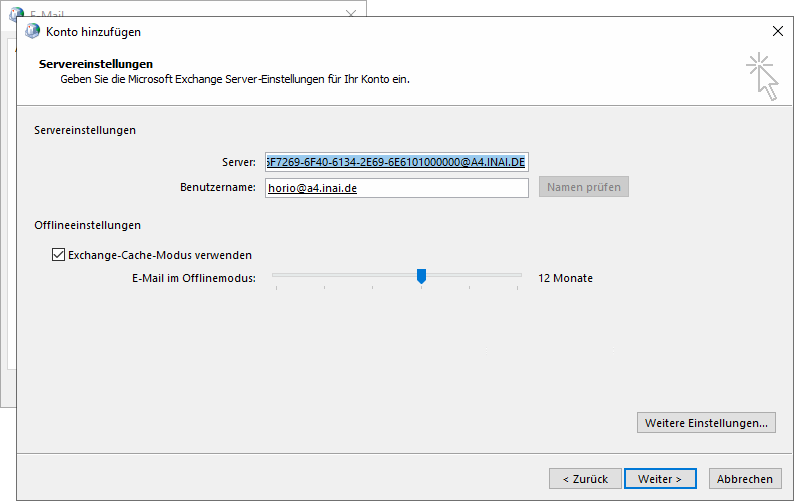
Repeatedly editing a field and using Check Names again, the profile wizard
ping-pongs between SERVERS and the endpoint ID.
To really fix the wrong RPC server name, using MFCMAPI will become necessary.
MAPI profile data model
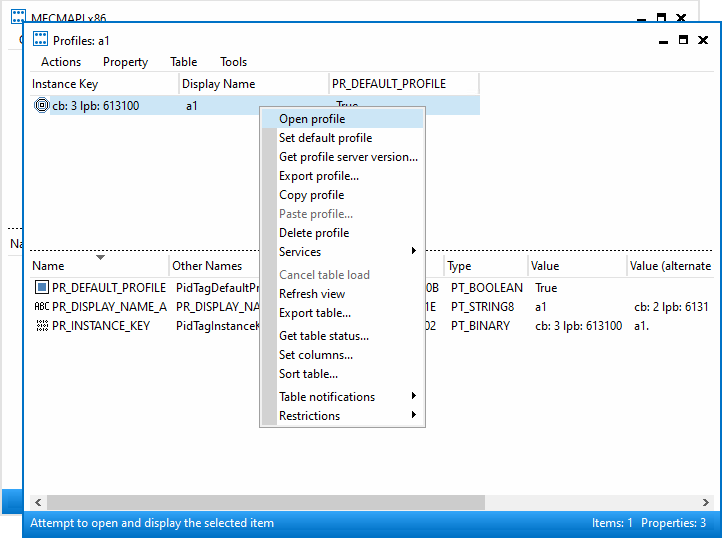
Inside the MAPI profile (a1 in the screenshots) are (at least) two
services, one of which is for the mailbox, and another is for the addressbook.
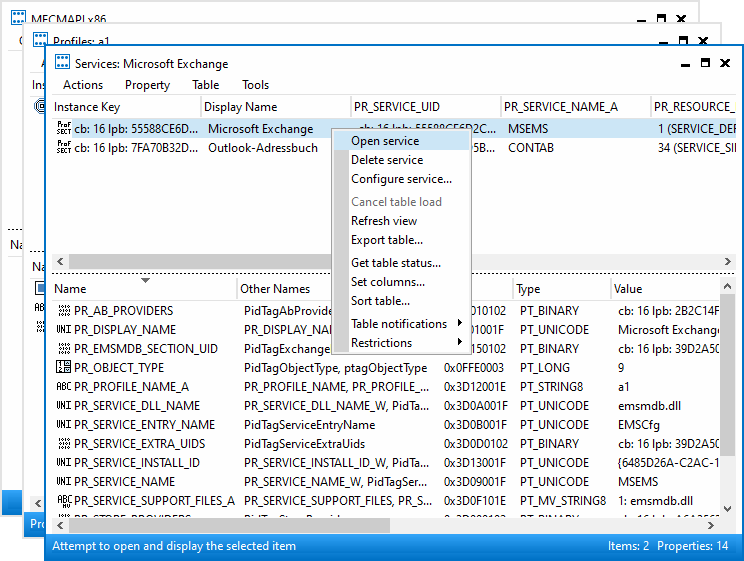
The EMSMDB service consists of three or four providers, these should correspond
to the private mailbox, the public mailbox (if any), a transport provider (XP),
and the global address book (GAB). The value SERVERS can be found in the
properties PR_TEST_LINE_SPEED (0x662B001F), and 0x662A001F.
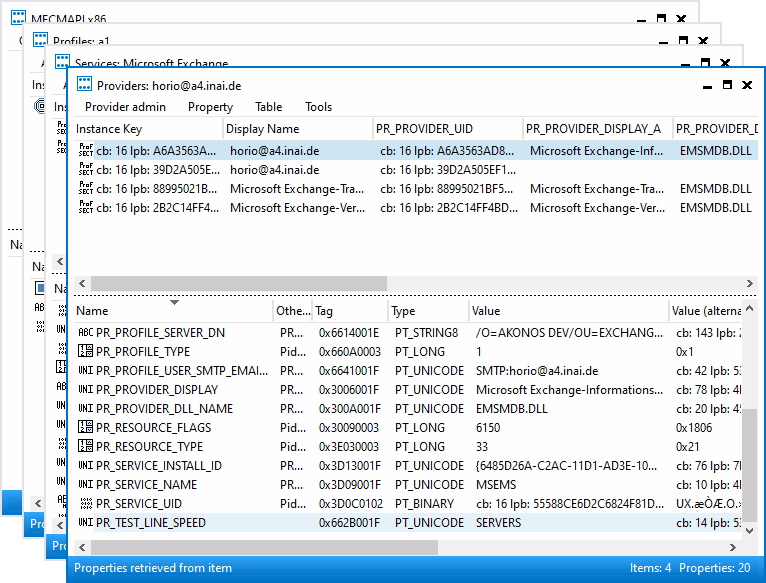
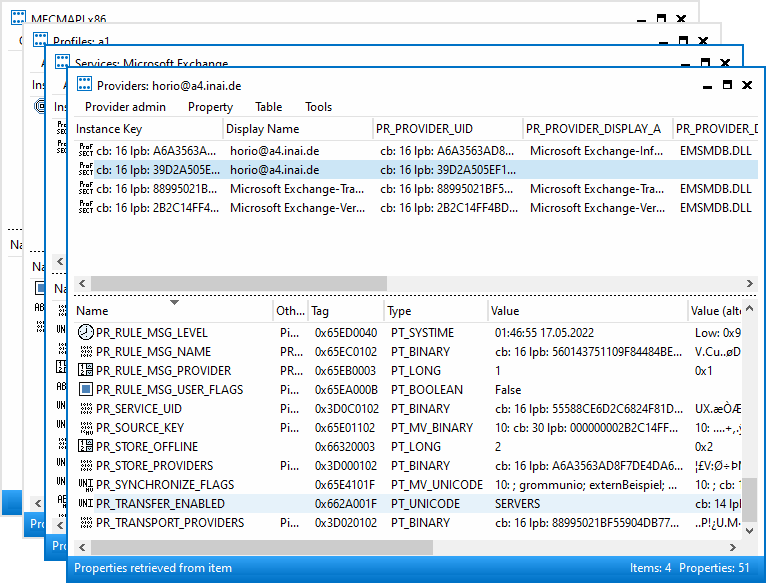
There is also PR_PROFILE_RPC_PROXY_SERVER (which contains the
RPCHTTP/MAPIHTTP proxy) and PR_PROFILE_UNRESOLVED_SERVER (unsure why this
is kept).
The value in the 0x662A001F property correlates with it. Changing this property in MFCMAPI changes it in the Control Panel dialog.
MFCMAPI shows the property as PR_TRANSFER_ENABLED, but that is not entirely
accurate. Some property IDs are — unfortunately — reused between different
components (e.g. profile vs. mailbox vs. address book), and MFCMAPI just does
not evaluate the context in which it is used, and so prints the wrong name.
The value for PR_TEST_LINE_SPEED is of no consequence. It is said
to be a special property to make emsmdb.dll always trigger a network request.
Changing SERVERS to the real host name makes mailbox access possible.
(Later versions of the connector such as from OL2021 do not create the 0x662A001F property at all anymore.)
Further reading
The Windows registry normally needs no changes, but for the curious, there are some options.
Technicalities with hanging connections
Outlook and tools like MFCMAPI usually invoke mapi32.dll functions from the same thread that also runs the user interface. The UI is blocked while MAPI functions execute. If the UI does not respond for a while, the desktop shell marks the window as unresponsive.
Modern connections to Exchange-style servers use HTTP (TCP), but even with a server sending TCP RST/FIN, the MSRPC libraries seem to take a while to notice. We surmise this is a side-effect of the historic design of DCERPC/MSRPC which allows for datagram transports — and where connection-oriented transports are an afterthought.
In Cached Mode, MAPI calls from application terminate at the OST file. The OST<->server synchronization runs in a separate thread. Therefore, connectivity interruptions do not normally affect the UI, though complex queries involving the OST contents (opening a folder with 50000 mails) may still.
In MFCMAPI with an online-mode MAPI profile, on connectivity interruption it can be observed that the store handle "shuts down" and a number of subsequent MAPI calls return a network error, until such a time that mapi.dll or the program decides to effectively re-login and obtain a new, valid store handle. (In doing so, MFCMAPI crashes sometimes. Outlook seems to handle this better and live on.)